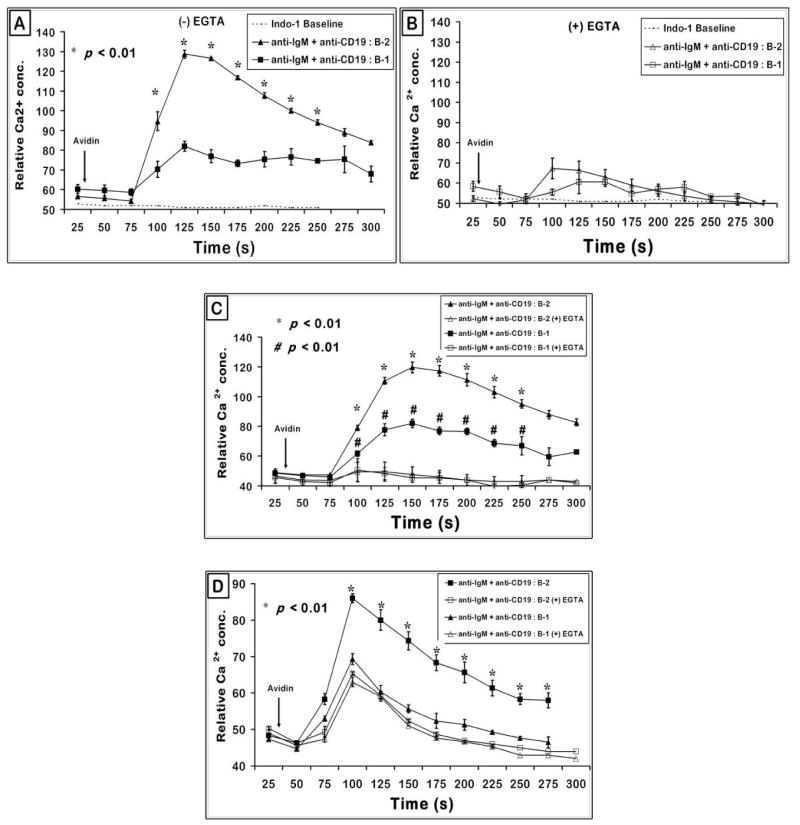
Figure 3. Effect of chelating extracellular calcium with EGTA on B cells stimulated with BCR and CD19.
(A and B) BCR and CD19 induced intracellular Ca2+ response appears to be similar in both splenic B-1 and B-2 cells. C57BL/6 spleen cells were treated as in Fig. 2 and gated on splenic B-1 (B220+ CD43+) and B-2 cells (B220+ CD43−) (Panel A). To obtain intracellular Ca2+ flux, cells were resuspended in media containing 6 mM EGTA to chelate extracellular Ca2+ available in the media (Panel B). Data shown is representative of one out of four independent experiments. Graph is plotted with data of mean + SE from triplicate samples. p < 0.01 compares the B-2 cell response to the B-1 cell response at each time point indicated.
(C and D) Biotinylated anti-IgM and biotinylated anti-CD19 co-cross-linking induced intracellular Ca2+ flux in VH12 negative littermate control mice is similar in splenic B-1 and B-2 cells. Splenic cells from VH12 negative littermate control mice (panel C) and transgenic mice (panel D) were treated similar to wild type splenic cells as in (panel A) and intracellular Ca2+ flux obtained as described above. Data plotted is mean + SE from triplicate samples. p < 0.01 comparing the response from B-2 cells with and without EGTA.