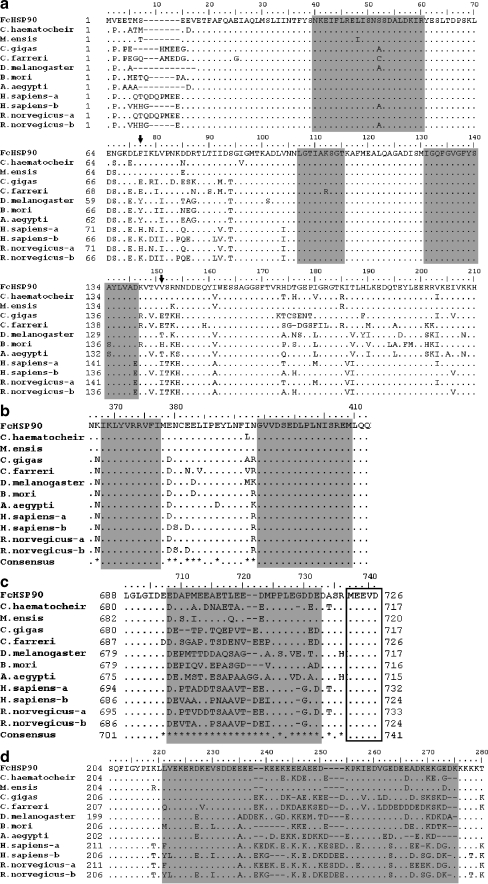
Fig. 2.
Homology analysis of FcHSP90 deduced amino acid sequence aligned by Bioedit 7.0. a The alignment of N domain of HSP90s. Three HSP90 protein family signatures are shaded with gray background. Arrows indicate phenylalanine (F, 77) and valine (V, 151) presenting homology divergence. b The alignment of M domain of HSP90s. Two HSP90 protein family signatures are shaded with gray background. c The alignment of C terminus of HSP90s. The residues shaded are variable parts located at the C terminus of HSP90s. The conserved “MEEVD” motif is boxed. d The link segment between N and M domain. The variable part is shaded with gray background. Residues identical to FcHSP90 at the same point in alignment are replaced by dot. Consensus sequence is produced: dots indicate at the point that all residues are identical and asterisks indicate that there are variations. Abbreviations and accession numbers are shown as follows: FcHSP90, F. chinensis HSP90, EF032650; C. haematocheir, C. haematocheir HSP90, AAS19788; M. ensis-HSP90, M. ensis HSP90, ABR66910; C. gigas, C. gigas HSP90,ABS18268; C. farreri, C. farreri AAR11781; D. melanogaster-HSP90, D. melanogaster HSP90, NP_523899; B. mori, B. mori HSP90, BAB41209; A. aegypti, A. aegypti HSP90, XP_001649752; H. sapiens-a and -b H. sapiens HSP90α, NP_005339, H. sapiens HSP90 β,NP_031381; R. norvegicus-a and –b, Rattus norvegicus HSP90α, NP_786937, R. norvegicus HSP90β, P34058)