Table 1.
Effects of DIP and DEC on colony size and determination of the half-life of wild type and variant Rob proteins
| Addition to lactose tetrazolium plates containing 0.2% or 2% arabinose |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No treatment |
DIP (1 mM) |
DEC (3 mM) |
||||||
| Rob Allele | Representative Western Blot | Half-life | 0.2% | 2% | 0.2% | 2% | 0.2% | 2% |
| None | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal | ||
| Wild type |
|
>20 hr | normal | normal | SMALL | NO GROWTH | SMALL | NO GROWTH |
| RobR40A |
|
>20 hr | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal |
| Rob107 |
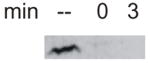
|
<1 min | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal |
| Rob249 |

|
20 min | normal | SMALL | normal | SMALL | normal | SMALL |
| SoxS-Rob |
|
>20 hr | normal | normal | NO GROWTH | NO GROWTH | NO GROWTH | NO GROWTH |
| SoxS | 2 min | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal | normal | |
Overnight cultures of strain RA4468 [pBAD18-Rob] carrying different rob alleles were diluted10−6 and 0.1 ml plated on lactose tetrazolium plates with 0.2% or 2% arabinose along with DIP (1 mM), or DEC (3 mM). Growth phenotypes were determined after incubating the plates at 37°C for 15 hr. In separate experiments, the half-life of the respective proteins was determined by western blotting. The half-life of native SoxS27 was determined previously and the value is included here.
