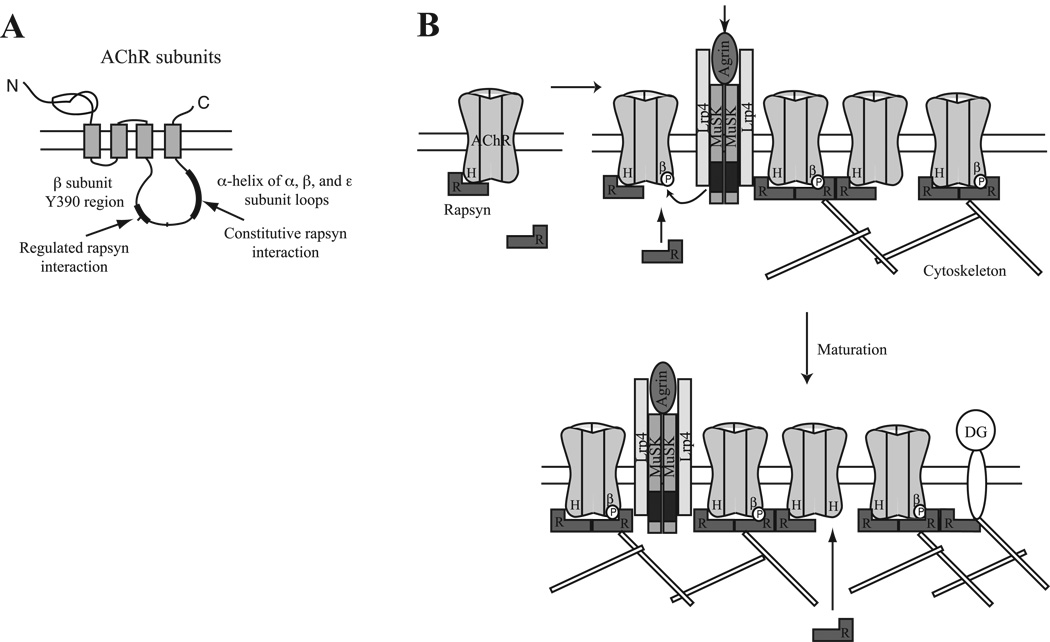
Figure 7. Model for AChR localization involving constitutive and regulated interactions with rapsyn.
(A) Schematic showing the subunit major intracellular loop regions involved in constitutive and regulated interactions with rapsyn. (B) We propose a model where unclustered AChR is constitutively associated with one rapsyn (R), via binding to the α-helical domain (H) in the β, ε or α subunit intracellular loop. Upon MuSK activation, tyrosine phosphorylation of the AChR β subunit (βP) induces binding of a second rapsyn to some receptors. Additional rapsyn binding may also occur during synapse maturation, via unoccupied sites on AChRs, dystroglycan (DG) or other cytoskeletal proteins. Changes in the stoichiometry of rapsyn binding regulate anchoring and stability of the AChR, modulating receptor levels and density in the postsynaptic membrane.