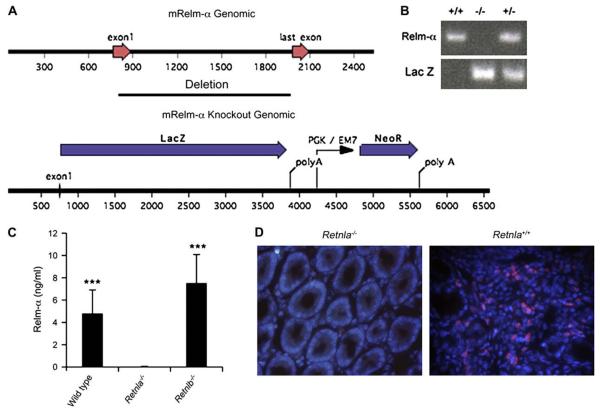
FIG 2.
Generation of Retnla−/− mice. The Retnla gene was replaced by a reporter-selection cassette, which consists of β-galactosidase and a neomycin resistance gene. The diagram shows the wild-type murine Retnla gene locus and the gene-targeted locus. The construct deletes all 4 exons of the Retnla gene (A). The mice were identified as heterozygotes and homozygotes by means of the Taqman assay with probes for LacZ genes and the Retnla loss-of-allele probes. Each lane represents a separate animal (B). Sera of wild-type, Retnla−/−, and Retnlb−/− mice were subjected to ELISA (C). ***P < .001 when comparing with Retnla−/− mice (n = 8-10 mice). Validation of anti–Relm-α antibody specificity and Retnla deficiency was obtained by means of immunofluorescent staining of a DSS-treated colon sections of Retnla−/− mice (D). mRelm-α, Murine Relm-α.