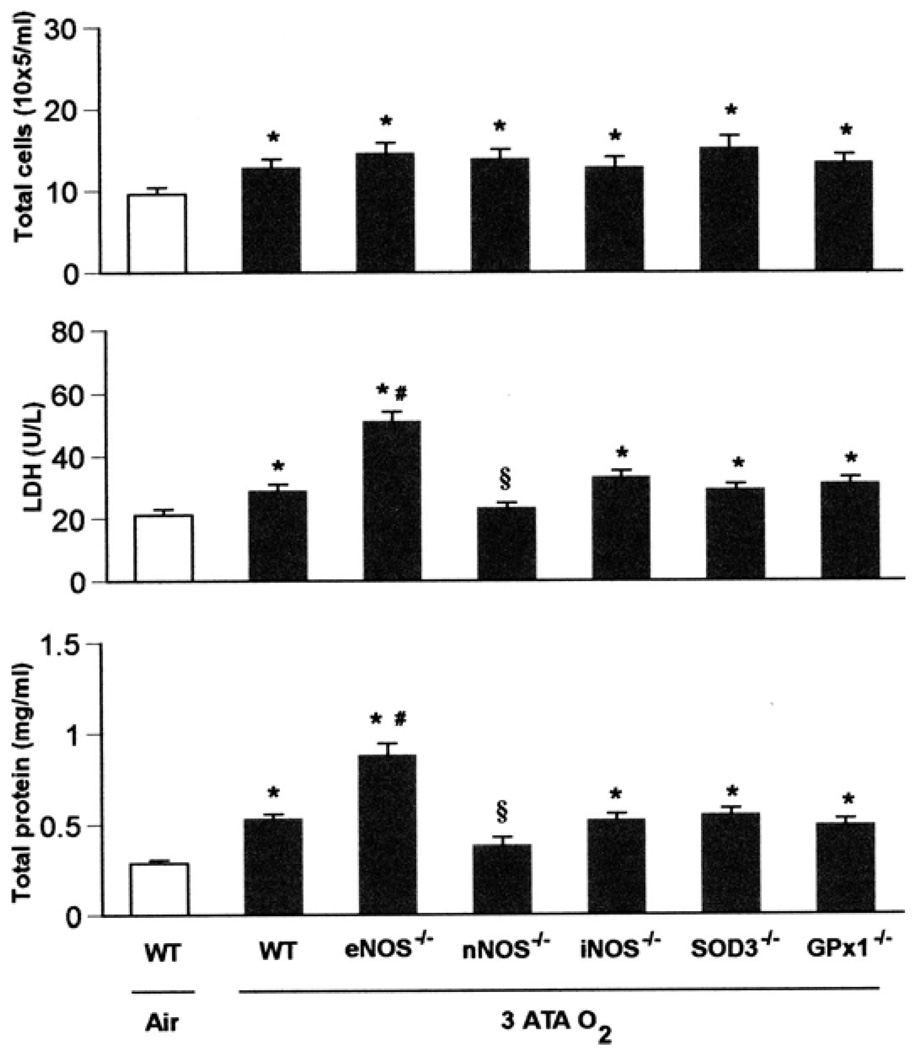
Fig. 2.
Pulmonary oxygen toxicity in 3 ATA O2. WT, eNOS−/−, nNOS−/−, iNOS−/−, SOD3−/−, and GPx1−/− mice (n = 10, 10, 10, 8, 8, and 8, respectively) exposed to oxygen at 3 ATA for 6 h experienced severe lung damage across all 3 indices of injury compared with WT mice (n = 3) breathing air (*P < 0.05 vs. WT in air). Although the nNOS mutants had significant increases in total cells, they showed no differences in protein and LDH compared with WT mice breathing room air. Mice deficient in eNOS had significantly increased LDH activity and total protein concentration in BALF after exposure to 3 ATA O2 compared with WT mice [#P < 0.05 vs. WT in hyperbaric hyperoxia (HBO2)], whereas nNOS−/− mice showed less LDH activity and total protein in BALF than WT in HBO2 (§P < 0.05 vs. WT in HBO2). The remaining knockouts (iNOS−/−, SOD3−/−, and GPx1−/−) showed lung injury similar to that of WT mice after 3 ATA O2.