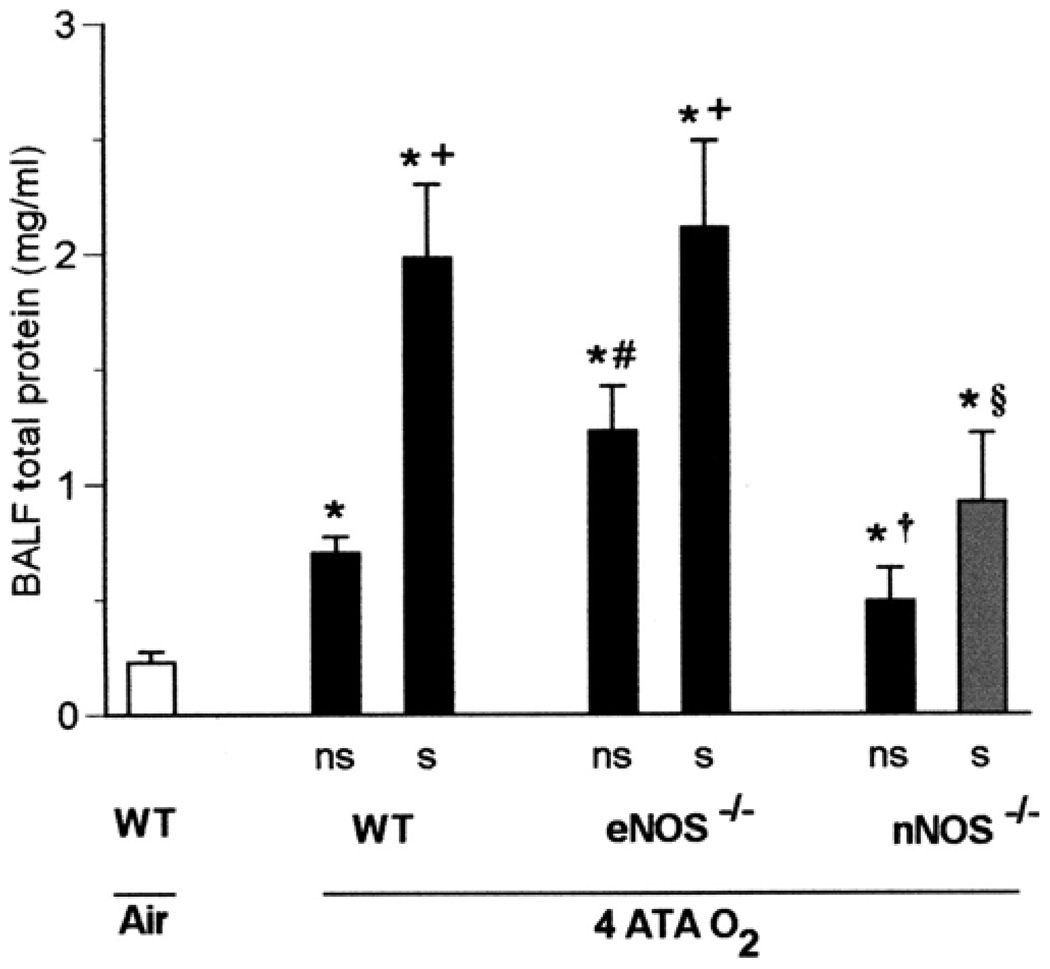
Fig. 3.
Seizures and pulmonary oxygen toxicity in 4 ATA O2. Total protein was measured in BALF as a marker of lung injury in WT, eNOS−/−, and nNOS−/− mice (n = 13, 12, and 11, respectively) exposed to 4 ATA O2 for 2 h. Protein content was significantly higher in all animals that exhibited seizures (s) (8 WT, 5 eNOS−/−, and 5 nNOS−/−) as well as in those without seizures (ns) than in WT mice (n = 4) breathing air (*P < 0.05 vs. WT in air). However, differences in total protein between ns and s mice of the same genotype were significant only in WT and eNOS−/− mice (+P < 0.05 vs. ns). Among animals without seizures, eNOS−/− mice had significantly greater BALF total protein than did WT animals (#P < 0.05 vs. WT ns), whereas decreases in total protein in nNOS−/− mice had borderline significance (†P = 0.05 vs. WT ns). The nNOS−/− mice with seizures were significantly protected compared with WT or eNOS−/− individuals, as indicated by total protein in BALF (§P < 0.05 vs. WT s or eNOS−/− s).