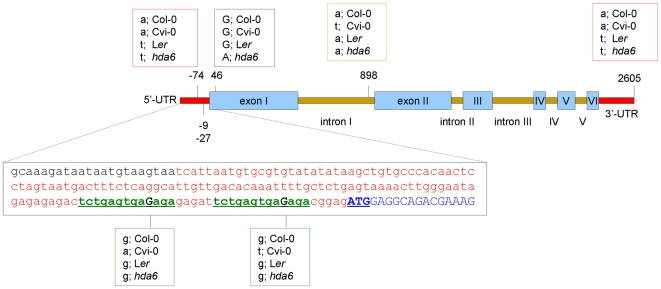
Figure 8. Cvi-0 has HDA6 5′-UTR polymorphisms compared to Ler and Col-0.
Schematic representation of the HDA6 (At5g63110) genomic sequence alignment in; Col-0, Cvi-0, Ler, and hda6 sil1/not. Untranslated regions (UTR; red), exons (blue boxes), and introns (orange bars) are shown along with the identified polymorphisms in bp relative to the ATG start codon. Hda6 represents the hda6 sil1/not mutant. Sequences were aligned using CLUSTAL W 2.0 multiple sequence alignment and the alignment produced using EMBL EBI tools. The zoom-in box shows the sequence of the HDA6 5′-UTR (red) and the start of the first exon (blue, start codon; bold/underlined). The small repeat sequences that harbor the polymorphism in Cvi-0 relative to Col-0 and Ler are shown in green (underlined) and the polymorphism site is shown in dark green. Note a G/A nucleotide substitution at bp 47 in the hda6 sil1/not mutant, which results in a predicted amino acid change from glycine (G) to arginine (R) in the hda6 sil1/not allele, confirming the results of Probst et al. [56]. Polymorphisms did not influence histone deacetylase signatures (as found using the NASC genome browser and extracting motifs using the SPRINT Prints view) nor potential miRNA targets, from http://sundarlab.ucdavis.edu/cgi-bin/mirna/.