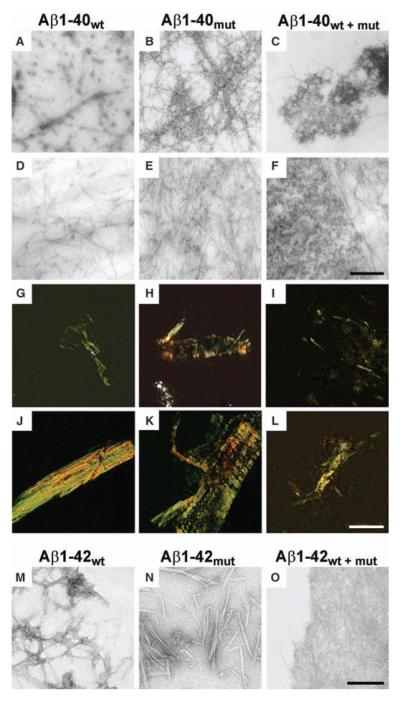
Fig. 3.
Aggregation properties of mutated and wild-type Aβ peptides. (A to F) Electron micrographs of aggregates generated by Aβ1-40wt, Aβ1-40mut, and equimolar mixtures after 72 hours [(A) to (C), negative staining] and 20 days incubation [(D) to (F), positive staining]. (G to L) Polarized light microscopy of Aβ aggregates stained with Congo red after 72 hours [(G) to (I)] and 20 days [(J) to (L)]. (M to O) Electron micrographs of negatively stained aggregates generated by Aβ1-42wt (M), Aβ1-42mut (N), and equimolar mixtures (O) after 5 days incubation. The peptide mixture contains mainly amorphous material (O), whereas wild-type and mutated Aβ1-42 are assembled in fibrillary structures. Scale bars indicate 250 nm [(A) to (F)], 50 μm [(G) to (L)], and 125 nm [(M) to (O)].