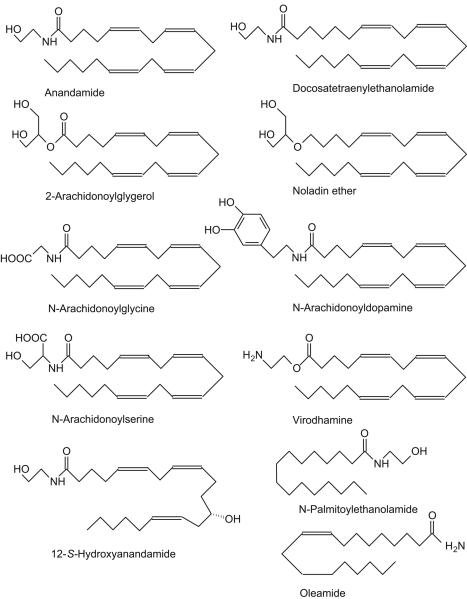
Figure 1.
Structures of the major endocannabinoids identified to date; most are based on the 20-carbon fatty acid, arachidonic acid though palmitoylethanolamide (the activity of which as an endocannabinoid is controversial) and the CB1 cannabinoid and TRPV1 agonist, oleamide, are exceptions with shorter chain lengths. The most frequently studied is anandamide (an agonist at CB1 and CB2 receptors as well as TRPV1 channels), which with 2-arachidonoylglycerol (an agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors with generally higher efficacy than anandamide11) is found to occur in many tissues of the cardiovascular system, including the heart and blood cells (especially platelets and monocytes). 12-S-hydroxyanandamide, which activates CB1 receptors, is synthesized by 12-lipoxygenase from anandamide taken up by platelets.21 Since 12-S-hydroxyanandamide is not a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase, then conversion of anandamide to this oxygenated derivative might have the effect of prolonging signaling due to anandamide synthesis.