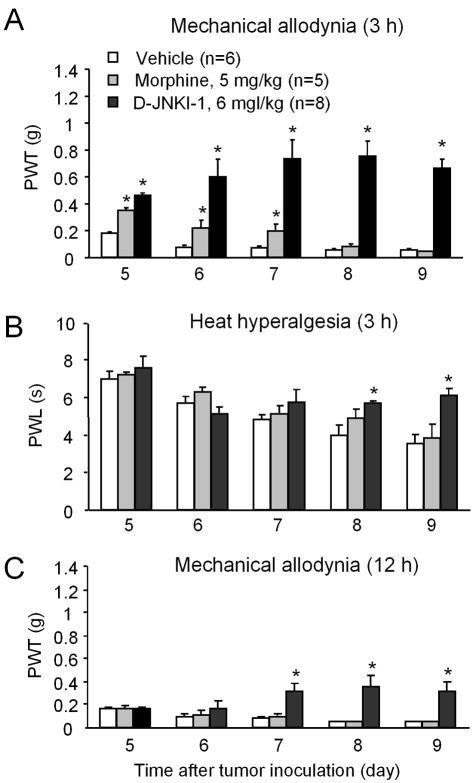
Figure 5.
Inhibition of melanoma-induced cancer pain by systemic injection of the JNK inhibitor D-JNKI-1. (A, B) Repeated injections of D-JNKI-1 (2 μmol or 6 mg/kg, i.p., twice a day) inhibit melanoma-induced mechanical allodynia as measured by paw withdrawal threshold (A) and heat hyperalgesia as measured by paw withdrawal latency (B). As comparison, repeated injections of morphine (8 μmol or 5 mg/kg, i.p., twice a day) only produce mild inhibition of mechanical allodynia with rapid development of tolerance. Pain behavior was tested 3 hours after the previous injection. (C) Repeated injections of D-JNKI-1 (6 mg/kg, i.p., twice a day) but not morphine (5 mg/kg, i.p., twice a day) also inhibit melanoma-induced mechanical allodynia when tested 12 hours after the previous injection. *P<0.05 vs. vehicle (PBS) control. Drugs were injected intraperitoneally twice daily from day 5 to 9 after tumor inoculation. Note accumulating effects of D-JNKI-1 on cancer pain after repeated injections.