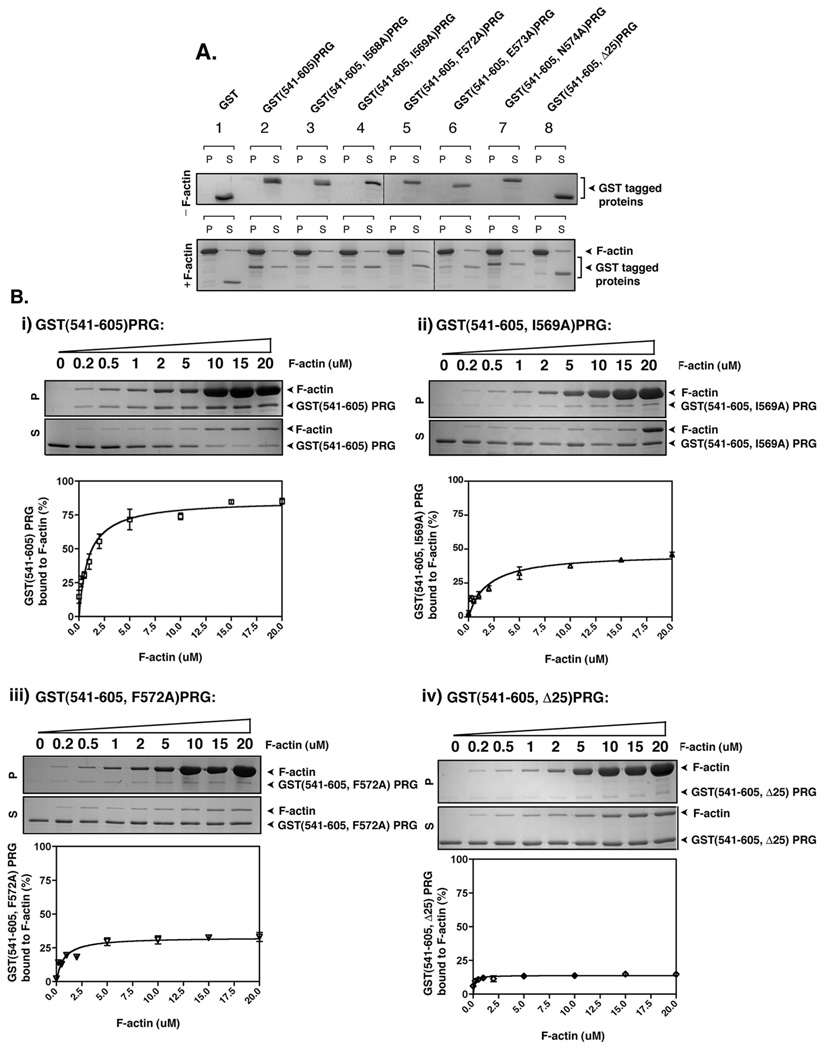
Figure 5. PRG binds to F-actin in vitro.
(A) 2 µg of the indicated recombinant proteins was incubated with or without 40 µg of freshly polymerized F-actin at room temperature for 30 min and then centrifuged at 160,000g for 90 min. Equal aliquots of resuspended pellet (P) and supernatant (S) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and colloidal blue staining. (B) Quantification of F-actin binding activity of recombinant PRG mutants, GST(541–605)PRG (i), GST(541–605, I569A)PRG (ii), GST(541–605, F572A)PRG and (iv) GST(541–605, Δ25)PRG. 3 µM of the indicated mutants of PRG were incubated with variable concentrations F-actin (0.2 – 20 µM) and co-sedimented at 160,000g for 90 min. Equal aliquots of resuspended pellet (P) and supernatant (S) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and colloidal blue staining (upper panels), and the bands were quantified by densitometry. The percentage of F-actin bound PRG mutants was calculated as the percentage recovered in the pellet (P) over total protein (S+P). The graphs represent the means ±S.D. of three independent experiments.