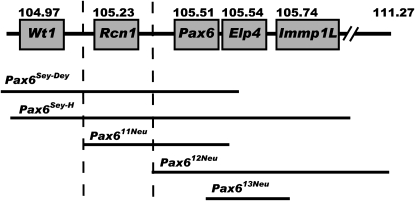
Figure 4.—
Schematic overview of the deleted regions in the Pax6Sey-Dey, Pax6Sey-H, Pax611Neu, Pax612Neu, and the Pax613Neu deletions. Pax6 and the proximal genes Wt1 and Rcn1 as well as the distal genes Elp4 and Immp1L are shown with their proximal end position in Mb (Ensembl build 51). The Pax6Sey-Dey deletion begins most proximal, includes Wt1, Rcn1, Pax6, and Elp4, and is estimated to be 1.2 Mb. The Pax6Sey-H deletion includes Wt1, Rcn1, Pax6, Elp4, and Immp1L, extends much further distally, and is estimated to be 2.9 Mb. The Pax611Neu deletion begins distal to Wt1 and proximal to Rcn1, extends into Elp4, and is 540 kb. Since the Elp4 gene is orientated tail to tail to the Pax6 gene the 3′ end of the Elp4 gene is deleted. The Pax612Neu deletion begins distal to Rcn1 and proximal to Pax6, extends furthest distally, and is 6.08 Mb long. The Pax613Neu deletion is 238 kb, begins within intron 6-7 of Pax6, extends through Elp4, and ends within the 5′ region of Immp1L. The critical region responsible for the extreme eye phenotype is marked by the broken lines.