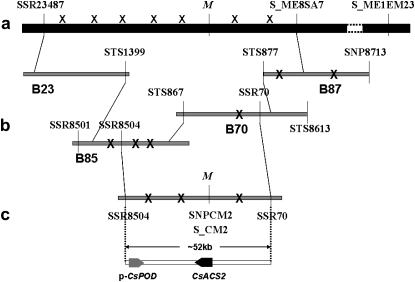
Figure 1.—
M map-based cloning. (a) M genetic map. “X” indicates recombination events identified in population 5234 (the “right side” of the M locus) and population 1983 (the “left side” of the M locus), respectively. (b) Fine mapping M. New marker SNP8713, derived from the B87 end sequence, was mapped beyond the M locus with an additional recombination event. SSR70 was developed from the B70 inner sequence, which was mapped at one recombination event from M between S_ME8SA7 and SSR23487. SSR8501 and SSR8504, derived from the B85, had three and two recombination events, respectively, from the M locus at the other side beyond the SSR70 marker. The final contig was confirmed by an overlap test from STS877, STS867, and STS1399. BAC clones were not drawn to scale. (c) The final contig and the genomic organization for this region. A contig encompassing the M locus, which included three recombination events, was identified by the two markers, SSR8504 and SSR70. Broad arrows indicate the two predicted genes (p-CsPOD and CsACS2) and the predicted transcriptional orientations. Two new markers, S_CM2 and SNPCM2, were developed from the candidate gene CsACS2 and cosegregated with the M locus. The primer sequences are listed in Table S2.