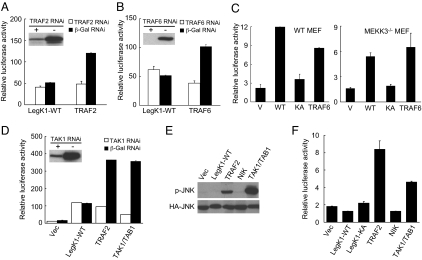
Fig. 3.
Signaling components upstream of the IKK complex are not required for LegK1-induced NF-κB activation. (A, B, and D) Luciferase assays of LegK1-induced NF-κB activation in TRAF2 (A), TRAF6 (B), and TAK1 (D) siRNA knockdown cells. The immunoblots (Inset) show the siRNA knockdown efficiency of the corresponding proteins, and TRAF2, TRAF6, and TAK1/TAB1 expression plasmids were used as positive controls. (C) LegK1-induced NF-κB luciferase activation in MEKK3−/− MEF cells. Wild-type (Left) or MEKK3−/− (Right) MEF cells were transfected with indicated plasmid together with the NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmid. V, WT, and KA refer to vector, LegK1-WT, and LegK1-KA mutant, respectively. (E and F) Effects of LegK1 expression on JNK activation. HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression constructs together with HA-JNK (E) or the JNK luciferase reporter plasmid (F). Activation of the JNK pathway was analyzed by phospho-JNK immunoblotting (E) or luciferase reporter assays (F).