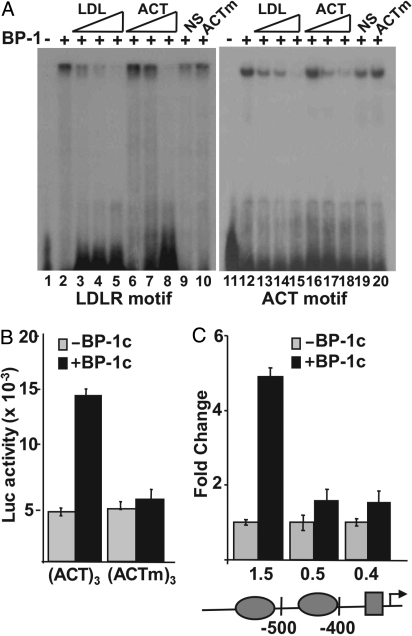
Fig. 3.
Functional analysis of the previously undescribed SREBP-1 binding motif. (A)32-P–labeled probes representing the well-characterized SREBP site from the human LDL receptor promoter (lanes 1–10) or the previously undescribed SREBP-1 motif (lanes 11–20) were incubated with buffer (lanes 1 and 10) or with recombinant SREBP-1 [BP-1 (2 ng), lanes 2–10 and 12–20] and analyzed by EMSA. Increasing concentrations of unlabeled probe (30-, 100-, or 300-fold molar excess) for either LDL receptor (LDL, lanes 3–5 and 13–15) or for the previously undescribed motif (ACT, lanes 6–8 and 16–18) were included in the binding reactions as indicated. In lanes 9 and 19, or 10 and 20, 300-fold molar excess of a nonspecific (NS) DNA fragment or a mutant version of the previously undescribed motif probe (ACTm) was included in the binding reaction. DNA sequences for probes and competitors are provided in Table S1. (B) Reporter plasmids containing 3 copies of the previously undescribed motif upstream of an Sp1 site (ACT)3 or a similar plasmid containing 3 copies of a mutated version (ACTm)3 were fused to the luciferase coding sequence and analyzed by transient transfection in 293T cells. The reporters were cotransfected with the pcDNA3.1 empty vector (gray bars) or an SREBP-1c expression vector (black bars). (C) Luciferase vectors for the WT and deleted versions of the GSK3a promoter were also prepared and analyzed for SREBP-1 responsiveness as above. The 3 promoter constructs contain a 1.5-, 0.5-, or 0.4-kb 5′ flanking sequence as indicated. The ovals on the promoter diagram denote positions of the 2 copies of the 5′-ACTACANNTCCC-3′, and the rectangle marks the position of an Sp1 consensus site.