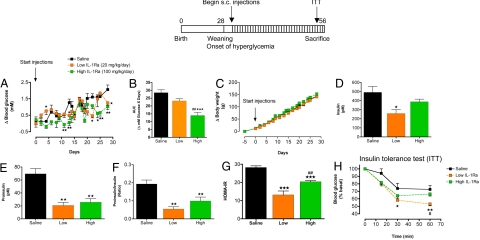
Fig. 3.
IL-1Ra treatment reduces hyperglycemia, reduces the circulating proinsulin/insulin ratio, and improves insulin sensitivity in the GK rat. Four-week-old male GK rats were injected s.c. twice daily with saline (n = 7; GK saline), 10 mg/kg/injection (n = 5), or with 50 mg/kg/injection IL-1Ra (n = 8; GK IL-1Ra) for 4 weeks as shown in the scheme. Animal groups had similar starting blood glucose values (see text). (A) Delta (Δ) fed blood glucose, (B) area under the curve (AUC) for Δ fed blood glucose values over 4 weeks of treatment, and (C) Δ body weight during treatment are shown. At the end of treatment (D) circulating fed insulin, (E) proinsulin, and (F) the proinsulin/insulin ratio were determined. (G) HOMA-IR was calculated, and (H) an insulin tolerance test (0.35 unit/kg) was performed at the end of treatment with saline or IL-1Ra. n represents the total number of animals treated in 2 separately conducted experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 compared to saline control. #, P < 0.05; ##, P < 0.01 compared to low-dose IL-1Ra as determined by ANOVA with Newman–Keuls posthoc analysis.