Figure 4.
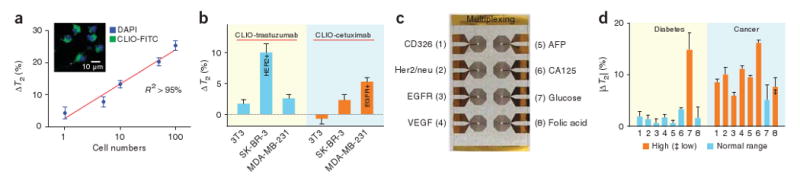
Profiling of mammalian cells. (a) Mouse macrophages (RAW 264.7) were incubated with magnetic nanoparticles (CLIO-FITC; inset) to determine cellular detection thresholds. A single cell in a 10- μl sample volume could be detected. (b) Cancer cell profiling by targeting cell surface markers. Magnetic nanoparticles conjugated with monoclonal antibodies to target Her2/neu and EGFR (CLIO-trastuzumab and CLIO-cetuximab, respectively) were incubated with breast cancer cells (positive control) or fibroblast cells (3T3, negative control). A larger decrease in T2 was observed with cell lines that overexpressed the targeted surface makers (SK-BR-3 for Her2/neu and MDA-MB-231 for EGFR). The measurements were performed on ∼1 × 104 cells in a 10-μl sample volume. (c,d) Detection of multiple biomarkers. A prototype microcoil array was designed for eight multiplexed measurements and detection targets were assigned (c). Magnetic nanoparticles for each target were conjugated with the corresponding antibodies or proteins. Normal, diabetic and cancer sera were prepared by adding the relevant markers to serum (Supplementary Table 4). Analysis of sera (d) shows the detection of abnormally high amounts of biomarkers in the samples; abnormally low amount of folic acid was detected in cancer serum as indicated by ‡. ΔT2 is shown as mean ± s.e.m. VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; AFP, α-fetoprotein; CA125, cancer antigen-125.
