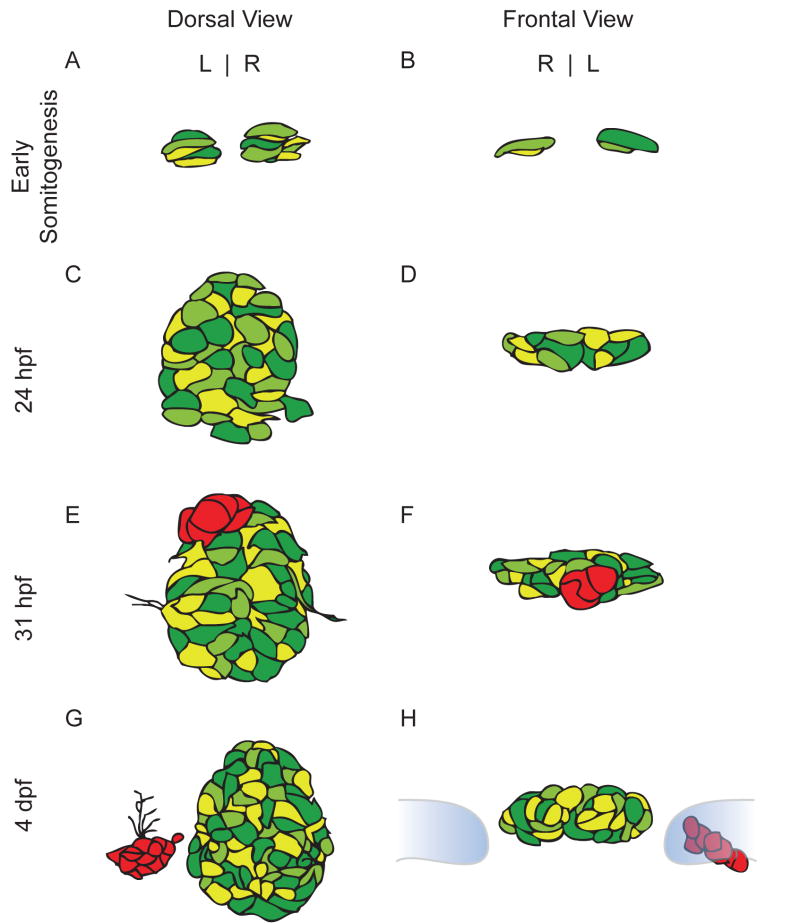
Figure 2.
Schematic drawings of pineal complex development from somitogenesis through embryogenesis. Drawings are based on expression of the foxd3:GFP transgenic line. Different shades of green indicate varying levels of transgene expression within the pineal organ. (A) Dorsal and (B) frontal views of the pineal complex during early somitogenesis. (C) and (D) The pineal complex at 24 h prior to the emergence of the parapineal. (E) and (F)The parapineal (red) forms as a group of cells in the anterior region of the pineal complex and is beginning to undergo the morphological changes that will result in two separate organs. (G) Dorsal view of a 4 d wild type embryo. The parapineal (red) has completed its migration. (H) A frontal view of the 4 dpf pineal complex. The habenulae are depicted in blue and outlined in grey. The parapineal (red) is located adjacent to the left habenula.