Abstract
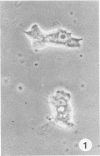
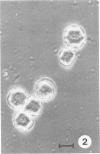
Two strains of amoebae, one (CDC:0180:1) from the lung tissue of a patient who died of granulomatous amoebic encephalitis and the other (CDC:0179:1) from the debrided tissue of a mandibular autograft, were isolated and identified as Acanthamoeba castellanii based on the morphological and immunofluorescent staining characteristics of the trophozoites and cysts. Both strains of amoebae caused cytopathic effects in mammalian cell cultures and destroyed the cell sheet. However, only the CDC:0180:1 strain, on intranasal instillation into mice, produced the disease manifested by ruffled fur and aimless wandering, followed by coma and death within 30 days. The CDC:0180:1 strain also differed consistently from CDC:0179:1 and another nonpathogenic A. castellanii strain (ATCC 30,011) in isoenzyme makeup, a dissimilarity which probably reflects its pathogenic potential.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borochovitz D., Martinez A. J., Patterson G. T. Osteomyelitis of a bone graft of the mandible with Acanthamoeba castellanii infection. Hum Pathol. 1981 Jun;12(6):573–576. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callicott J. H., Jr, Nelson E. C., Jones M. M., dos Santos J. G., Utz J. P., Duma R. J., Morrison J. V., Jr Meningoencephalitis due to pathogenic free-living amoebae. Report of two cases. JAMA. 1968 Oct 14;206(3):579–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland P. G., Lawande R. V., Onyemelukwe G., Whittle H. C. Chronic amebic meningoencephalitis. Arch Neurol. 1982 Jan;39(1):56–57. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510130058016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key S. N., 3rd, Green W. R., Willaert E., Stevens A. R., Key S. N., Jr Keratitis due to Acanthamoeba castellani. A clinicopathologic case report. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980 Mar;98(3):475–479. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1980.01020030471005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez A. J. Acanthamoebiasis and immunosuppression. Case report. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1982 Sep;41(5):548–557. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198209000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez A. J. Is Acanthamoeba encephalitis an opportunistic infection? Neurology. 1980 Jun;30(6):567–574. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.6.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez A. J., Sotelo-Avila C., Garcia-Tamayo J., Morón J. T., Willaert E., Stamm W. P. Meningoencephalitis due to Acanthamoeba SP. Pathogenesis and clinico-pathological study. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Mar 31;37(3):183–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00686877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page F. C. Re-definition of the genus Acanthamoeba with descriptions of three species. J Protozool. 1967 Nov;14(4):709–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Neal R. A. A comparative study of Entamoeba histolytica (NIH :200, HK9, etc.), "E. histolytica-like" and other morphologically identical amoebae using isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Shulman S. T., Lansen T. A., Cichon M. J., Willaert E. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis: a report of two cases and antibiotic and immunologic studies. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):193–199. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Balamuth W. Comparative studies on related free-living and pathogenic amebae with special reference to Acanthamoeba. J Protozool. 1975 May;22(2):245–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb05860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Callaway C. S. Light and electron microsopic observations on the pathogenesis of Naegleria fowleri in mouse brain and tissue culture. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Smith P. D., Healy G. R., Brown W. R. An immunofluorescence test to detect serum antibodies to Giardia lamblia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Dec;93(6):802–805. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-6-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willaert E., Stevens A. R., Healy G. R. Retrospective identification of Acanthamoeba culbertsoni in a case of amoebic meningoencephalitis. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Aug;31(8):717–720. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.8.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]