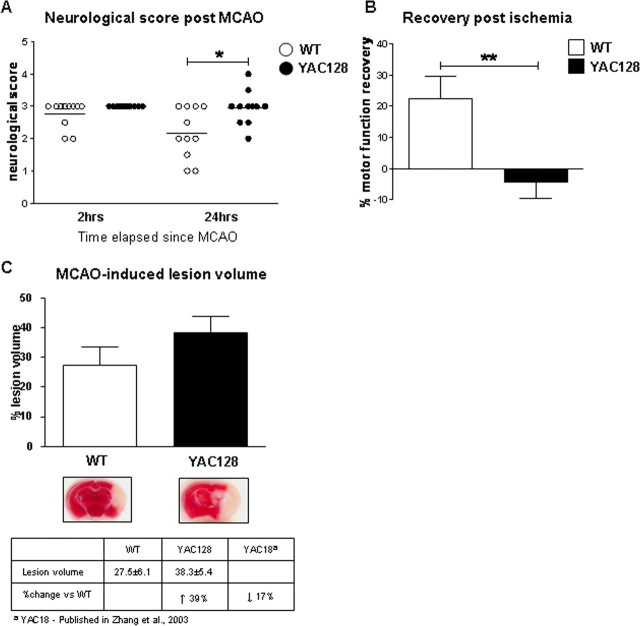
Figure 2.
Mutant huntingtin exacerbates neuronal dysfunction after stroke injury. A, Assessment of motor function in 1.5-month-old YAC128 (HD53) and WT mice 24 h after ischemia-induced injury reveals the presence of mhtt delays the recover of motor function in YAC128 (HD53) mice compared with WT (p < 0.05). No difference between genotypes is observed for baseline gross sensorimotor behavior 2 h after stroke injury. B, Percentage recovery from MCAO is significantly reduced in YAC128 (HD53) mice versus WT (p < 0.01). In contrast to WT mice, which demonstrate an improvement in motor function 24 h after ischemia (23%), YAC128 (HD53) continue to perform poorly (−4%). C, Representative images of infarct volume in YAC128 (HD53) versus WT coronal sections reveal the ischemic-induced damage by TTC staining. Quantification of lesion volume demonstrates a 39% increase in YAC128 (HD53) compared with control which approaches statistical significance (p < 0.09). Lesion volume is ±SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.