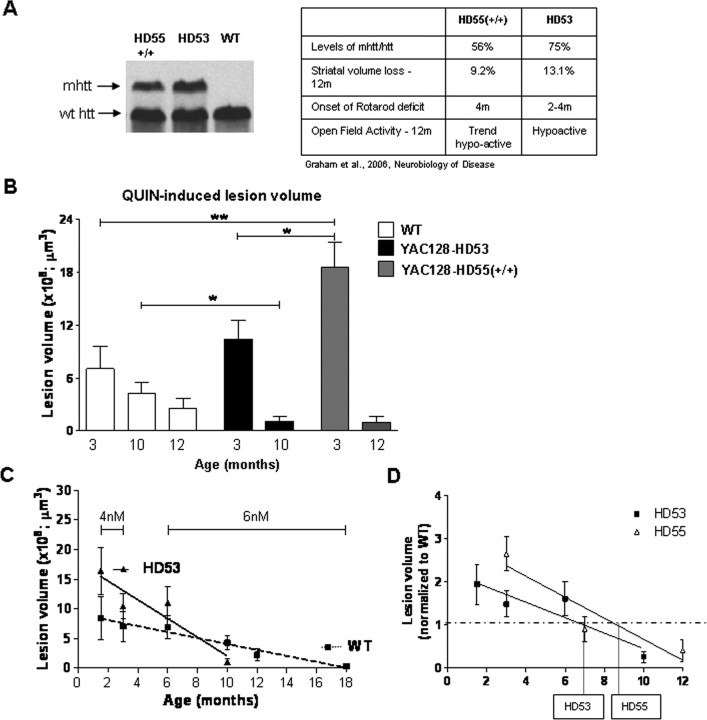
Figure 4.
Susceptibility to excitotoxic stress in YAC128 mouse models of HD is dependent on the stage of the HD phenotype. A, Levels of mhtt in YAC128 line HD55+/+ and HD53. A more severe phenotype is observed in the higher mhtt expressing line HD53. B, The presence of mhtt influences the response to QUIN-induced neurotoxicity with initial enhanced sensitivity to excitotoxic stress progressing to resistance later in the phenotype. HD55+/+ demonstrate an increase in lesion volume versus WT at 3 months of age (p < 0.01) and a trend toward resistance at 12 month. HD53, which demonstrates enhanced sensitivity at 1.5 months, are resistant to QUIN-induced excitotoxicity at 10 months of age (p < 0.05). A significant difference is observed in lesion volume between HD55+/+ and HD53 at 3 months of age (p < 0.05). C, Linear regression analysis reveals an increased rate of progression of the excitotoxic phenotype is observed in HD 53 mice as revealed by an increase in the slope of HD53 versus WT (p = 0.01). D, Onset of the resistance phenotype in HD53 occurs earlier than HD55+/+, at 6.9 and 8.6 months respectively. Lesion volume is ±SEM .*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.