Fig. 1. Complementation of a S. cerevisiae vps1 null mutant.
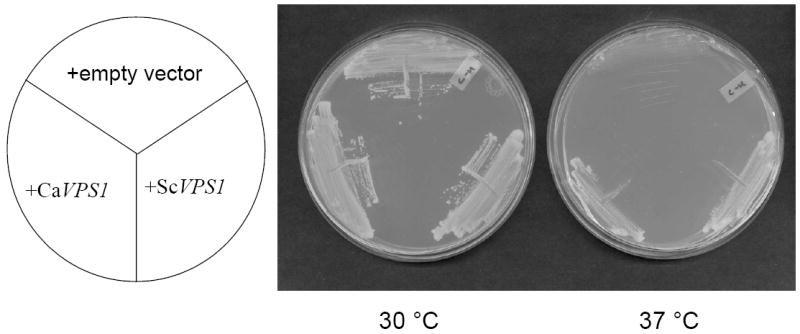
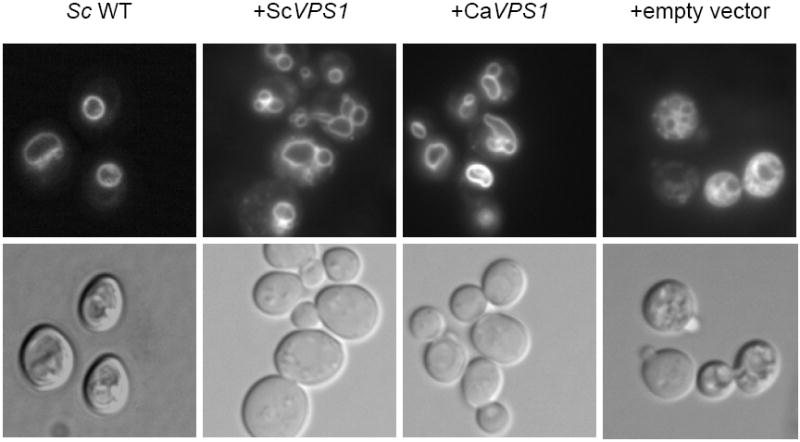
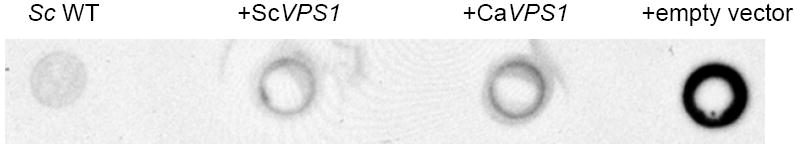
Over-expression of C. albicans VPS1 complements the temperature-sensitivity of a S. cerevisiae vps1 null mutant (A). Low copy number yeast shuttle plasmids (pRS316) containing C. albicans VPS1 (Ca VPS1) and S. cerevisiae VPS1 (Sc VPS1) conferred on a temperature-sensitive S. cerevisiae vps1 mutant the ability to grow at 37 °C, but empty vector alone did not. Over-expression of C. albicans VPS1 complements the S. cerevisiae vps1 null mutant vacuolar phenotype (B). Low copy number plasmids (pRS316) containing Sc VPS1, Ca VPS1, or no insert were introduced into a S. cerevisiae vps1 null mutant strain. Overnight cultures of strains grown in rich media were shifted to fresh media and examined during late exponential phase and stained with the vacuolar dye FM4-64. Live cells were examined by epifluorescence and DIC microscopy. The strain bearing vector alone displays a characteristic class “F” vacuolar morphology. Over-expression of C. albicans VPS1 complements carboxypeptidase (CPY) missorting of a S. cerevisiae vps1 null mutant (C). S. cerevisiae vps1 mutants missort CPY to the extracellular space, in contrast to wild-type strains, which do not. Therefore, overnight cultures of a S. cerevisiae wild-type strain and S. cerevisiae vps1 null mutant strains transformed with a vector bearing either Ca VPS1, Sc VPS1, or vector alone were spotted on solid media. Next, a colony immunoblot was performed by overlaying the spotted colonies with a nylon filter, followed by Western blotting using monoclonal antibody to S. cerevisiae CPY. A positive signal indicates missorting of CPY to the extracellular space.
