Fig. 4.
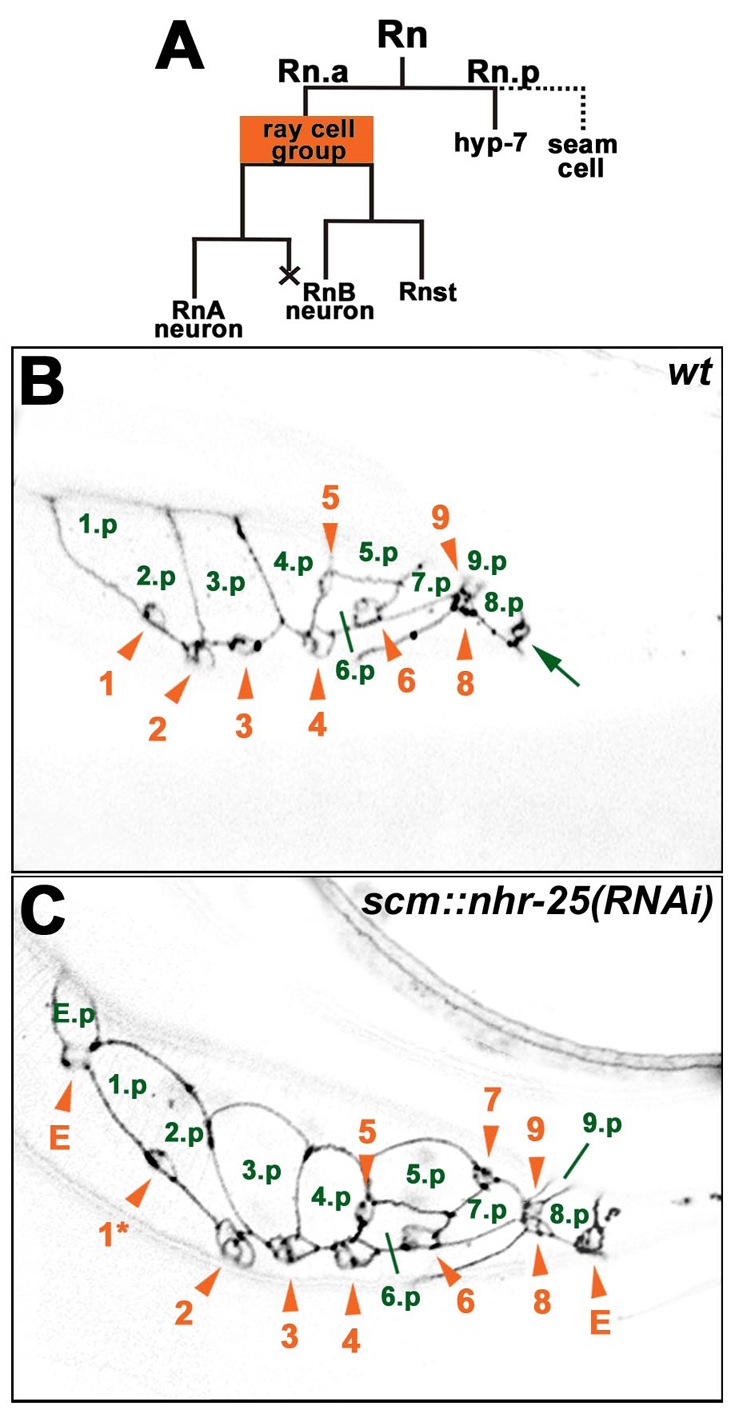
scm::nhr-25(RNAi) males display ectopic ray cell groups. (A) Lineage diagram of a ray cell cluster (Rn). An anterior Rn daughter produces a ray cell group, consisting of two neurons and one structural cell. The posterior daughter has a hypodermal character and it either fuses with the hyp7 syncytium (in the case of rays 6, 7, 8 and 9) or it fuses with other seam cells (1.p-5.p) to form a tail seam syncytium (SET). X represents programmed cell death. (B,C) Confocal sections show adherens junctions of ray cell clusters using the ajm-1::gfp transgene. The images of L4 males were taken approximately 40 hours after hatching. Signals were inverted for better clarity. Green numbers mark hypodermal Rn.p cells. The 1.p and 2.p cells are already fused, signifying formation of the SET syncytium. Ray cell groups are labeled with orange arrowheads and numbered in the order of the corresponding rays. Ray cell group 7 is out of the focal plane in wild type (B). (C) Males that are heterozygous for scm::nhr-25(RNAi) display an anterior ectopic ray cell cluster, which includes a ray cell group (E) and a hypodermal cell (E.p). Another ectopic ray cell group (E) is situated posterior to ray cell groups 8 and 9. Phasmid (arrow in B) is in another focal plane in C. In addition, displacement of ray cell group 1 is apparent (asterisk in C). Anterior is to the left.
