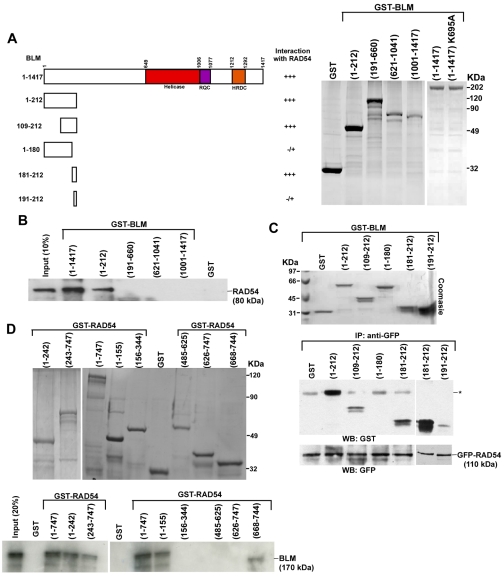
Fig. 2.
Internal residues of BLM interact with N- and C-termini of RAD54. (A) Summary of BLM-RAD54 interactions (left). Coomassie-blue-stained gel showing the expression of purified GST or GST-tagged BLM fragments BLM(1-212), BLM(191-660), BLM(621-1041), BLM(1001-1417), BLM(1-1417) and BLM(1-1417) K695A (right). (B) N-terminal region of bound GST-tagged BLM interacts with 35S-labeled full-length RAD54. After pull-down, bound radioactive RAD54 was determined by autoradiography. (C) A 10 amino acid stretch in the N-terminus of BLM interacts with RAD54. Bound GFP-RAD54 was incubated with soluble BLM fragments. After pull-down, the blots were probed with anti-GST and anti-GFP antibody. Asterisk indicates a crossreactive band migrating at the same molecular mass as BLM 1-212. (D) Coomassie-blue-stained gel showing the expression of purified GST or GST-tagged RAD54 fragments. Bottom gel shows that N- and C-terminal domains of RAD54 are required for its interaction with BLM. 35S-labeled full-length BLM was incubated with wild-type RAD54 or its various fragments.