Fig. 10.
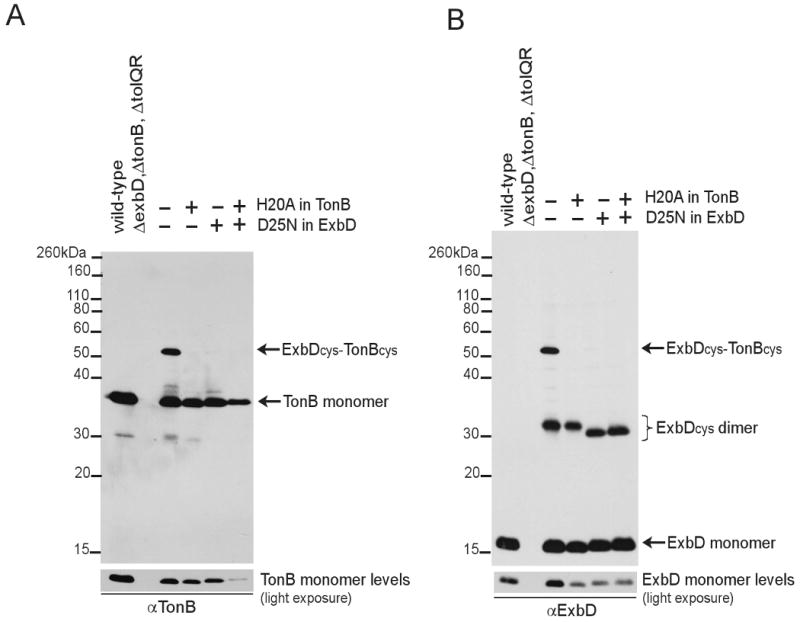
Active TonB and ExbD cysteine substitutions form specific periplasmic domain contacts. Strains expressing wild-type ExbD and TonB (W3110), ExbD(A92C) with TonB(C18G, A150) [KP1509/pKP1000, pKP945], ExbD(A92C) with TonB(C18G, H20A, A150C) [KP1509/pKP1000, pKP1031], ExbD(D25N, A92C) with TonB(C18G, A150C) [KP1509/pKP1049, pKP945] were processed in non-reducing sample buffer containing iodoacetamide as described in Materials and Methods. Samples were resolved on a 13% non-reducing SDS-polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted. ExbD (A) or TonB (B) was visualized with ExbD-specific polyclonal antibodies or TonB-specific monoclonal antibodies. Positions of molecular mass standards are indicated on the left. Lanes 3 through 6 contained strain KP1509 expressing derivatives of ExbD(A92C) coexpressed with TonB(C18G, A150C). Derivatives contained (+) or lacked (-) the residue substitutions listed to the right.
