Figure 3. Fos activation after AgRP neuron ablation is suppressed in some brain regions by bretazenil treatment.
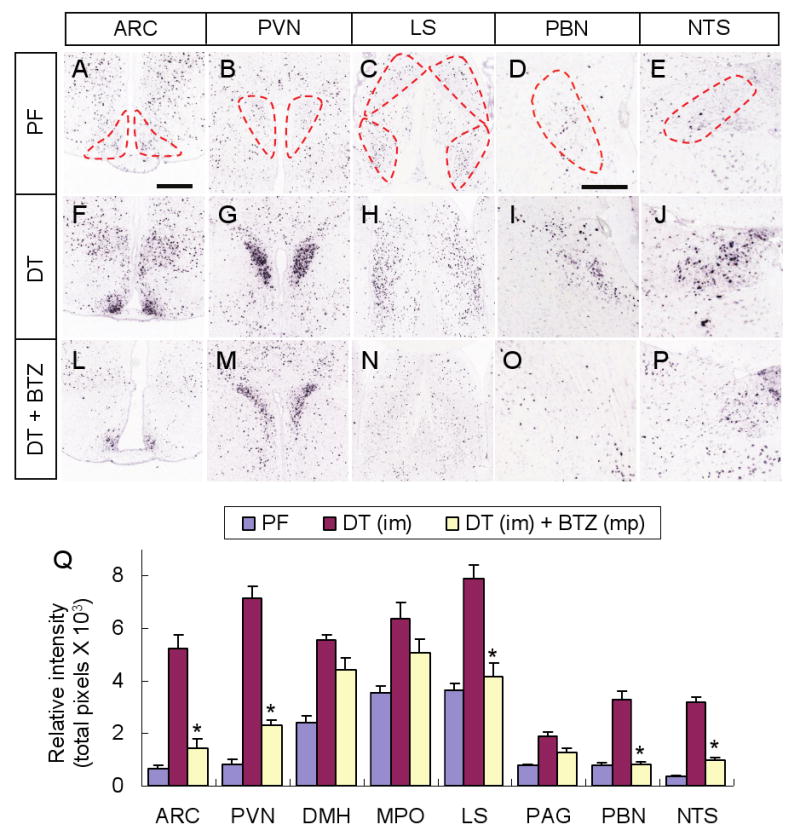
(A-E) Representative pictures of Fos in situ hybridization in post-synaptic regions of AgRP neurons including the ARC (A), PVN (B), LS (C), PBN (D), and NTS (E), in pair-fed AgrpDTR/+ mice after losing ∼20% of their initial body weight. Post-synaptic areas of AgRP neurons are denoted by dotted lines.
(F-J) Representative pictures of Fos in situ hybridization in the same post-synaptic regions of AgRP neurons in DT-treated, AgrpDTR/+ mice after losing ∼20% of their initial body weight.
(L-P) Representative pictures of Fos in situ hybridization in the same post-synaptic regions of AgRP neurons in DT-treated, AgrpDTR/+ mice with subcutaneous implantation of minipumps eluting bretazenil.
(Q) Quantified results for Fos in situ signals in selected post-synaptic regions of AgRP neurons of either pair-fed, DT-treated, or DT/bretazenil-treated, AgrpDTR/+ mice. See Supplementary Figure S6 for a complete set of images of Fos in situ hybridization in these regions. *, p < 0.01 between the DT-treated group and the DT/bretazenil-treated group for each respective area, ANOVA.
N = 4 - 6 per group. Scale bar (in A): A-C, F-H, and L-N, 400 μm; scale bar (in D): D, E, I, J, O, and P, 400 μm. Error bars in Q represent the SEM.
