Fig. 1.
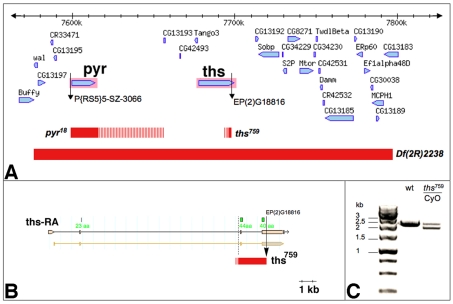
Genomic characterisation of single mutant alleles for ths and pyr. (A) Region of the Drosophila genome corresponding to cytological bands 48C1-48C4. Red bars indicate the extent of deletions in Df(2R)ED2238, pyr18 and ths759, as determined by PCR and RT-PCR mapping (striped bars mark regions containing breakpoints that have not been confirmed by sequencing). The pyr18 deletion extends to the insertion site of P[RS5]5-SZ-3066 proximally and excludes CG13193 distally. (B) ths759 deletes exon 3, the third intron and part of exon 4 of ths. This deletes 84 amino acids of the FGF core domain (regions that encode amino acids of the core domain are indicated in green). The distal breakpoint represents the insertion site of EP(2)G18816 and the proximal breakpoint is ∼300 bp 5′ of exon 3. (C) RT-PCR on polyA+ RNA from wild-type (wt) and ths759 heterozygous embryos showing a 2.4 kb band corresponding to the wild-type ths mRNA and an additional 1.9 kb band in ths759 heterozygotes. The 1.9 kb product was sequenced and corresponds to the deletion depicted in B.