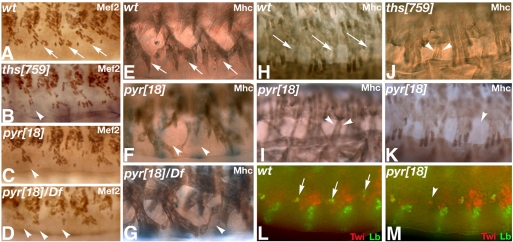
Fig. 6.
Requirement of FGF8-like ligands for the differentiation of specific subgroups of somatic muscles. (A-D) Ventral somatic muscle nuclei (stained for Mef2) in late stage Drosophila embryos. (A) Wild type (wt). Nuclei of ventral oblique (VO) muscles 4-6 are indicated by arrows. VO muscle nuclei are missing in a few hemisegments of ths759 homozygotes (B) and in several hemisegments of pyr18 homozygous (C) and hemizygous (D) embryos (arrowheads) (see also Table 1). (E-K) Myosin heavy chain (Mhc) staining showing somatic muscles in stage 17 embryos. (E-G) Ventrolateral views showing ventral muscles. One or more of VO muscles 4-6 (arrows in E, wild type) are missing in several hemisegments of pyr18 homozygous (F) or hemizygous (G) embryos (arrowheads). (H-K) Lateral views. Segment border muscles (SBMs) are indicated by arrows in the wild type (H). SBM duplications are observed in both pyr18 (I) and ths759 (J) homozygous mutants (arrowheads), and hemisegments lacking an SBM are also observed in pyr18 homozygotes (arrowhead in K). (L) Wild-type stage 10 embryo showing Lb expression (green) in the ectoderm and mesoderm. Arrows indicate segmental expression of Lb in the lateral mesoderm. (M) Lb expression in a pyr18 embryo showing absence of Lb-positive mesoderm cells in one hemisegment (arrowhead).