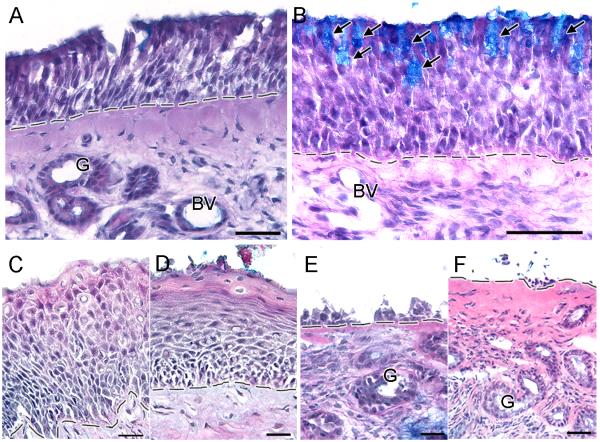
Figure 1.
Olfactory mucosa patterns observed in the biopsies of CRS patients. A. A normal pseudostratified human olfactory epithelium has a laminar organization consisting of an apical layer of olfactory supporting cells, several layers of immature and mature olfactory sensory neurons, and one or more layers of basal cells sitting on top of the basement membrane. Beneath the basement membrane is the lamina propria which is composed of connective tissue, mucus glands, blood vessels, olfactory axon bundles, trigeminal fibers and local immune cells. B. Goblet cell hyperplasia pattern is characterized by the presence of goblet cells intermixed with olfactory supporting cells in the olfactory sensory epithelium. C. Squamous metaplasia pattern is characterized by the transformation of the apical layers of cells into squamous-like layers. D. Flattening of squamous-like apical layers indicates severe squamous metaplasia pattern. E - F. Erosion pattern is characterized by various degrees of olfactory epithelium loss, leaving an exposed basement membrane. Arrows = goblet cells, G = glands, BV = blood vessel, dashed line = basement membrane. Scale bar: A and F = 40μm, B = 50μm, C-E = 20μm.