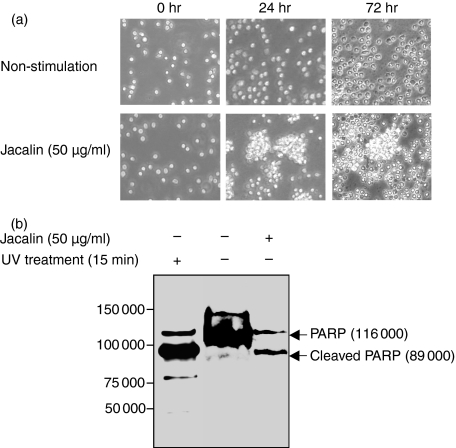
Figure 4.
Effects of Jacalin-stimulated human primary B lymphocytes. (a) Differential morphological changes of Jacalin-stimulated human primary B lymphocytes. The separated human CD19+ B cells were stimulated without (upper panels) or with (lower panels) Jacalin at 50 μg/ml for 24 and 72 hr, respectively. Photographs were taken after 24 and 72 hr stimulation using an Olympus microscope. (b) Determination of Jacalin-induced human primary B-lymphocyte apoptosis. The separated human CD19+ B cells were incubated without or with Jacalin at 50 μg/ml for 72 hr, followed by assessment of apoptosis. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage was analysed by Western blot for apoptosis detection. The arrows indicate 116 000 PARP (upper bands) and 89 000 apoptosis-related cleavage fragment (lower bands). As a positive apoptosis control, primary B cells were exposed to ultraviolet irradiation at 254 nm for 15 min.