Fig. 2.
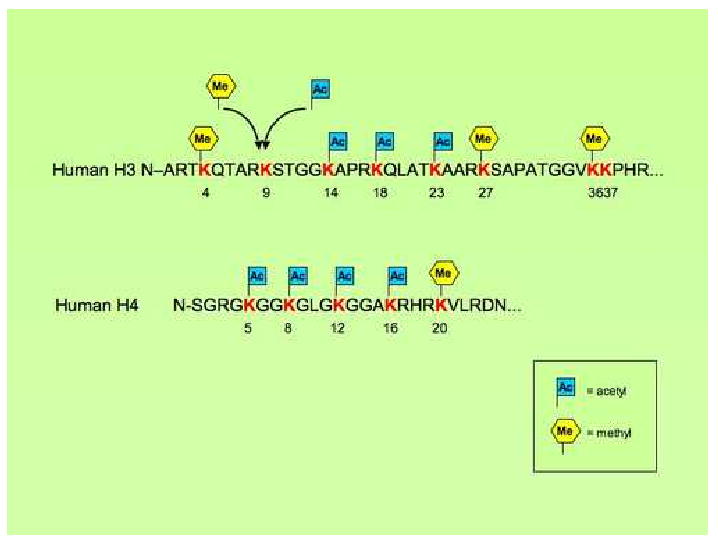
This figure shows the lysine residues in the amino terminus of the external tail of human histones H3 and H4 that can be susceptible to methylation and/or acetylation. Amino acids are reported in a single letter symbol. Numbers depict the lysines residues, which can either be methylated, or acetylated, with the only exception of lysine residue 9 in the tail of histone H3, where methylation and acetylation can both occur.
