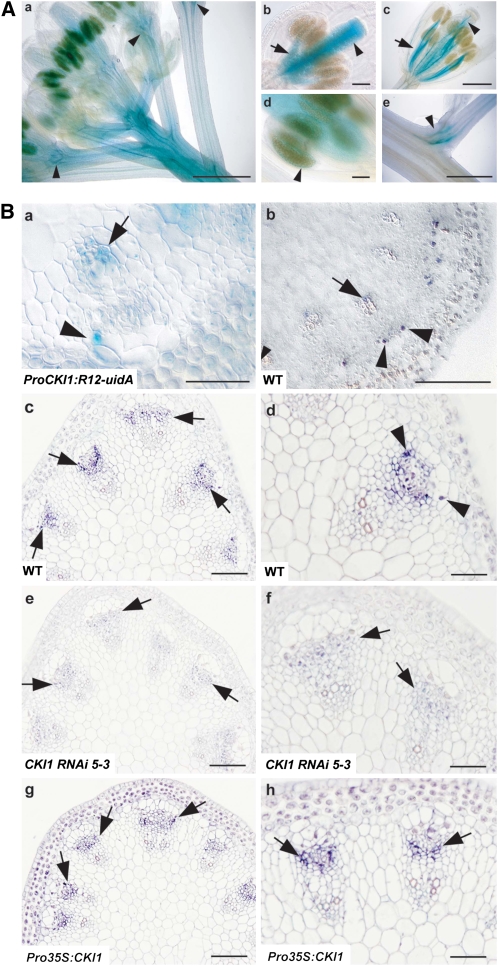
Figure 1.
Expression of CKI1 in VBs.
(A) GUS activity in flowering transgenic plants harboring ProCKI1:R12-uidA ([a] and [c] to [e]) or ProCKI1:uidA (b). (a) Top of the Arabidopsis inflorescence. Note the intensity of the signal in the subapical region of the inflorescence stem, vascular tissues of floral organs, and floral pedicels (arrowheads). (b) and (c) Floral organs before (b) and at/just after anthesis (c). Note the predominant GUS staining in the pistil in the flowers before anthesis ([b]; arowhead); conversely, the signal in the vascular tissue of stamens is stronger in flowers at/just after anthesis ([c]; arrow). (d) Male sporophytic tissue (arrowhead). (e) Axillary meristem. Bars = 500 μm in (a), (c), and (e) and 100 μm in (b) and (d).
(B) CKI1 expression in VBs of the inflorescence stem. (a) GUS staining in a cross section of the inflorescence stem of a ProCKI1:R12-uidA plant. GUS activity is seen in cells of the VB sheath located at the lateral (outer) borders of the VB (arrowhead) and xylem (arrows; see also [b]). (b) In situ localization of CKI1 mRNA. (c) to (h) In situ immunolocalization of CKI1 using αCKI1ED polyclonal antibodies in the cambium of VBs (deep-purple signal, arrows) on cross sections of inflorescence stems of wild-type ([c] and [d]), CKI1RNAi ([e] and [f]), and Pro35S:CKI1 plants ([g] and [h]). px, protoxylem; mx, metaxylem; arrowheads point to the strongest signal, located in cells on the outer border of the VB (cf. with [a] and [b]; arrowheads). Note the procambial localization of CKI1 even in the Pro35S:CKI1 line. Bars = 100 μm in (b), (c), (e), and (g) and 50 μm in (a), (d), (f), and (h).