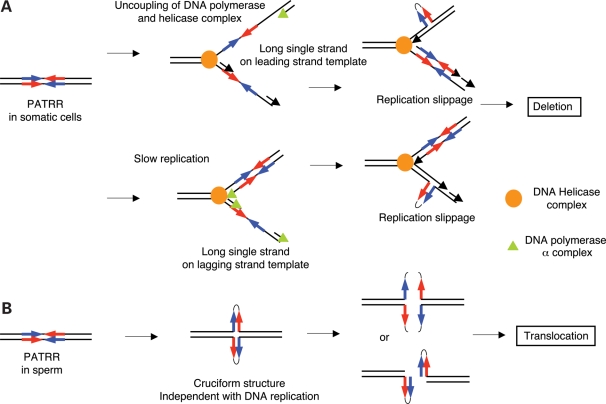
Figure 6.
Mechanism of palindromic instabilities in humans. (A) Slow DNA polymerase-induced deletion of the PATRR. Inhibition of DNA polymerase by siRNA or aphidicolin uncouples the helicase complex and DNA polymerase complex. Long single-strand DNA in the leading strand template facilitates a hairpin formation at the palindromic region that may induce deletion by slippage (upper panel). Slow replication also promotes long single-strand DNA in the lagging strand template that may lead to secondary structure formation at the palindromic region (lower panel). (B) PATRR-mediated translocation. The mechanism which dictates that translocation may be driven by DNA replication-independent cruciform structure.