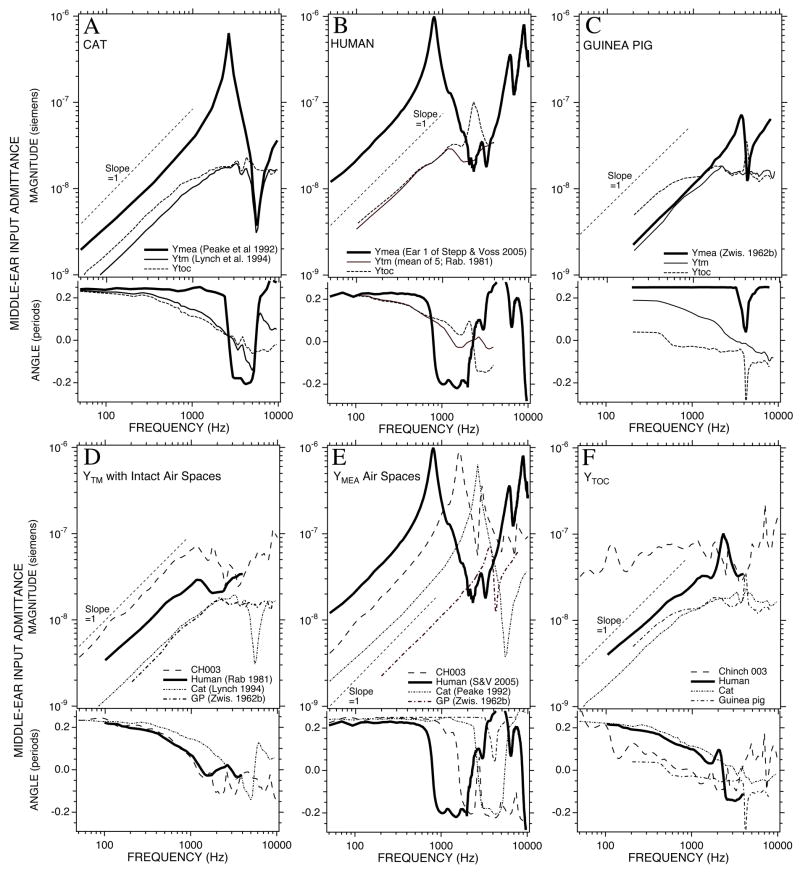
Figure 15.
Comparison of admittance measurements of intact ears, middle-ear cavities and computations of YTOC. (A) The middle-ear admittance in cat: the intact middle ear (Ytm, Lynch et al. 1994), the middle-ear air space admittance (Ymea, Peake et al. 1992) and YTOC. (B) The middle-ear admittance in human: the intact middle ear (Ytm, Rabinowitz et al. 1981), the middle-ear air space admittance (Ymea, Stepp & Voss 2006) and YTOC. (C) The middle-ear admittance in guinea pig: the intact middle ear (Ytm, Zwislocki 1963), the middle-ear air space admittance (Ymea, Zwislocki 1963) and YTOC. (D-F) Comparisons of the three admittance types with measurements in Chinchilla #003.