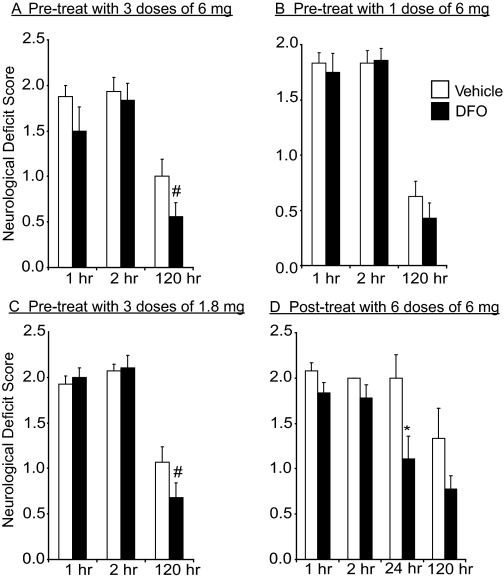
Fig. 3.
Intranasal DFO treatment reduces neurologic deficit score at 5 days or 48 h after middle cerebral artery occlusion (mean ± S.E.). Intranasal doses were administered under anesthesia. A, pretreatment with three 6-mg intranasal doses of 10% DFO (n = 9) compared with intranasally administered water control (n = 9). B, pretreatment with one 6-mg intranasal dose of 10% DFO (n = 14) compared with intranasally administered water control (n = 12). C, pretreatment with three 1.8-mg intranasal doses of 3% DFO (n = 14) compared with intranasally administered water control (n = 14). D, post-treatment with six 6-mg intranasal doses of 10% DFO (n = 9) compared with intranasally administered water control (n = 6). p values from Student's unpaired t test with #, p < 0.10 and *, p < 0.05.