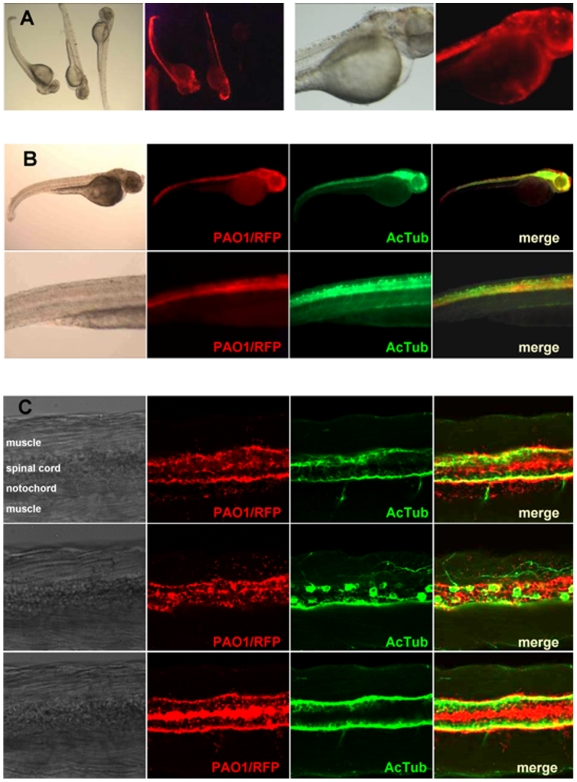
Figure 8. Localization of P. aeruginosa within zebrafish embryos.
(A) Fluorescent images of embryos at 1 dpi with an intermediate dose of P. aeruginosa PAO1/RFP cells overexpressing vreI from the pMUM3 plasmid. These embryos were highly infected and normally died by 24–30 hpi. Embryos in whose PAO1/RFP was not visible at 1 dpi (i.e. embryo at the right side of the first panel) survive by clearing the infection and were indistinguishable from the non-injected group. (B) Fluorescent images of embryos infected with PAO1/RFP (red channel) and subjected to whole mount immunohistochemistry using an anti-acetylated tubulin (AcTub) monoclonal antibody that specifically recognizes the nerves of the embryo (green channel). The last panel shows the red/green overlay. (C) Confocal images of three different focal planes of the embryo shown in (B) with similar color coding. All PAO1/RFP panels clearly show the concentration of P. aeruginosa in and around the spinal cord. In addition single bacteria can be seen in the muscle tissue. No colocalization of neuronal cell bodies or axons with PAO1/RFP was seen. However, a close contact between the axon tracts in the spinal cord and the PAO1/RFP is observed.