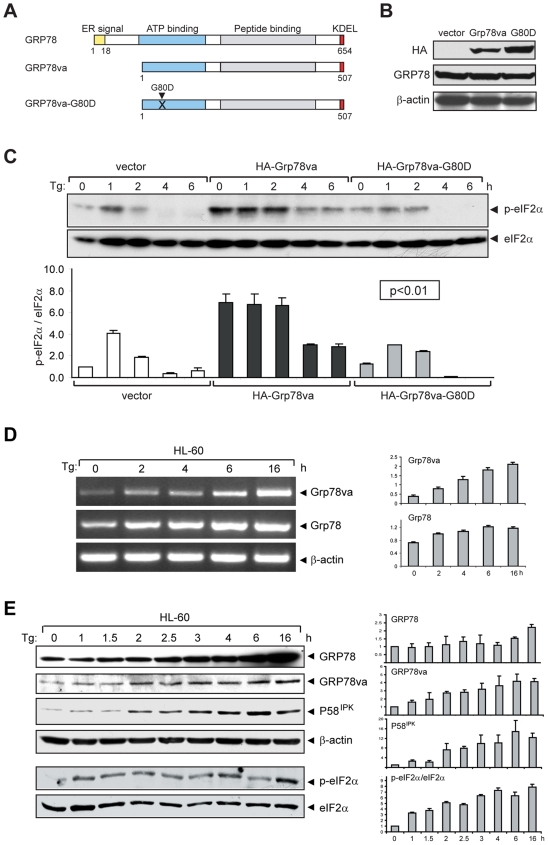
Figure 5. Mutation in ATP binding domain of GRP78va attenuates eIF2α phosphorylation.
A. Schematic representation of human GRP78, GRP78va, and the ATP binding mutant GRP78va-G80D. The position of mutation site is indicated. B. Western blots to detect ectopic expression of GRP78va and the mutant in stably transfected HeLa cell lines. The GRP78va proteins and endogenous canonical GRP78 were detected by the anti-HA and anti-GRP78 antibody respectively, with β-actin as loading control. C. Time course analysis of eIF2α phosphorylation in Tg-treated HeLa cells stably expressing HA-GRP78va or the mutant. Western blots were performed to determine total and phospho-eIF2α levels (upper panel). The ratio of phospho-eIF2α to total eIF2α from two independent experiments are summarized and expressed as the mean with the indicated standard deviation (SD) (lower panel). P values for all time points are indicated. D. Time course analyses of Tg induction of Grp78va and canonical Grp78 transcripts by RT-PCR. HL-60 cells were treated with Tg (300 nM) for the indicated time and the total RNA was subjected to RT-PCR (left panel). The experiments were repeated three times. The results are summarized and expressed as the mean of the normalized Grp78va or canonical Grp78 levels with the indicated SD (right panel). E. Time course analyses of Tg induction of canonical GRP78, GRP78va, P58IPK and eIF2α phosphorylation (p-eIF2α). HL-60 cells treated with Tg (300 nM) for the indicated time were used for Western blot for detection of the indicated proteins with β-actin as loading control (left panel). The experiments were repeated twice. The levels of canonical GRP78, GRP78va and P58IPK normalized to β-actin and the ratio of phospho-eIF2α to total eIF2α are summarized and plotted respectively (right panel).