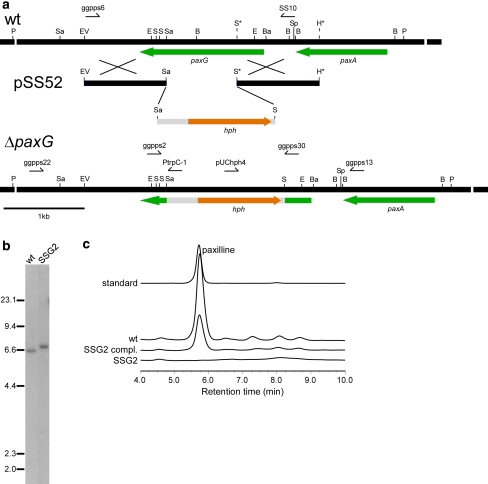
Fig. 3.
Deletion analysis of P. paxillipaxG. a Physical map of the P. paxillipaxG wild-type (wt) genomic region, linear insert of paxG-replacement construct pSS52 and P. paxillipaxG-deletion mutant (ΔpaxG) genomic region, showing the primers used for amplifying the linear replacement construct (primers ggpps6 & SS10) and screening gene integrations (primers ggpps2 & ggpps30, ggpps22 & PtrpC-1 and ggpps13 & pUChph4), and the restriction enzyme sites for BamHI (Ba), BglII (B), EcoRI (E), EcoRV (EV), HindIII (H), PvuII (P), SacI (Sa), SalI (S), and SpeI (Sp). The restriction sites marked by an asterisk are introduced by PCR for cloning. b Autoradiograph of a DNA gel blot of PvuII genomic digests (1 μg) of P. paxilli wild-type (wt) and ΔpaxG mutant strain SSG2 (PN2662) probed with [32P]-labeled paxG-replacement construct, amplified from pSS52 with primers ggpps6 and SS10. c Reverse-phase HPLC analysis of mycelia extracts of P. paxilli ΔpaxG mutant strain SSG2 (PN2662), SSG2 derivative strain (PN2663) (SSG2 compl.) and wild-type (wt)