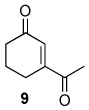
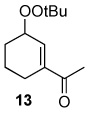
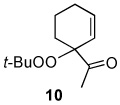
Table 2.
Oxidation of 1-acetylcyclohexene by TBHP in CD2Cl2 at 40 °C with various catalysts.a
| Catalyst | Oxidant | % Conversion b | % Yieldc | Relative %yieldd | Ratio (9 + 13)/10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|||||
| 0.5 mol % Rh2(cap)4 | 70 % TBHP in water | 80 | 71 | 27 | 34 | 39 | 1.6 |
| 0.1 mol % Rh2(cap) | 70 % TBHP in water | 80 | 63 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 2.3 |
| 0.5 mol % Rh2(cap)4 0.5 equiv. K2C03 | 6.7 M TBHP in decane | 82 | 49 | 45 | 22 | 33 | 2.0 |
| 2.0 mol % RuCl3•nH2O | 70 % TBHP in water | 59 | 42 | 21 | 38 | 40 | 1.5 |
| 2.0 mol % CuI | 70 % TBHP in water | 71 | 51 | 24 | 37 | 39 | 1.6 |
| 5.0 mol % Pd(OH)2 | 70 % TBHP in water | 38 | 36 | 17 | 50 | 33 | 2.0 |
| 5.0 mol % Pd(OH)2 0.25 equiv. K2CO3 | 70 % TBHP in water | 62 | 42 | 40 | 31 | 29 | 2.4 |
Reactions were performed with 1-acetylcyclohexene (0.27 M in CD2C12), using 4.0 equiv 70 % TBHP in D20 and the specified amount of catalyst with 1.0 equiv of biphenyl as internal standard. The reactions were performed in a standard NMR tube, heated to 40 °C, and were monitored by 1H NMR.
Percent conversion for each reaction was measured by the amount of 1-acetylcyclohexene remaining after 20 hours, relative to the internal standard.
Percent yield was determined by the sum of products formed after 20 hours, relative to the internal standard.
The results from duplicate runs were reproducible within 5 % of the reported values.
