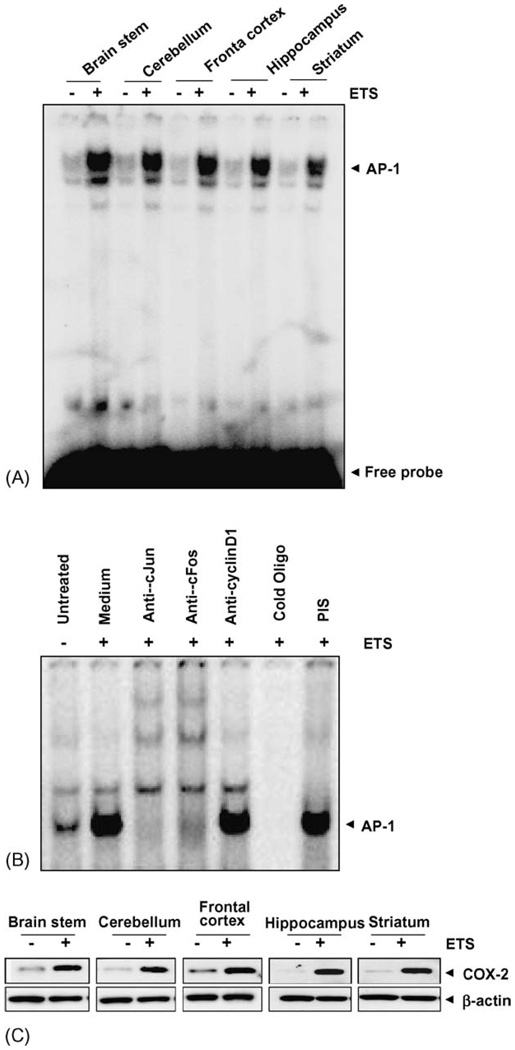
Fig. 3.
(A) ETS induces AP-1 activation. ETS increases AP-1 DNA binding in mice brain. Twenty micrograms nuclear proteins were analyzed in 6.6% native PAGE to detect AP-1 by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. The data shown is a representative of five independent experiments performed on extracts obtained from control and ETS exposed mice brain regions. (B) Supershift and specificity of AP-1 activation. Brain tissue extracts prepared from brain region of control and ETS exposed mice were incubated for 15 min with different antibodies, cold AP-1 oligonucleotides, and then assayed for AP-1, as described in Section 2. (C) ETS induces COX-2 activation in mice brain. Tissue extracts from different regions of brain were collected, 100 µg of the protein was analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE and detected for COX-2 using anti-COX-2 antibody by Western blot. The same blot was stripped off and re-probed with β-actin by Western blot.