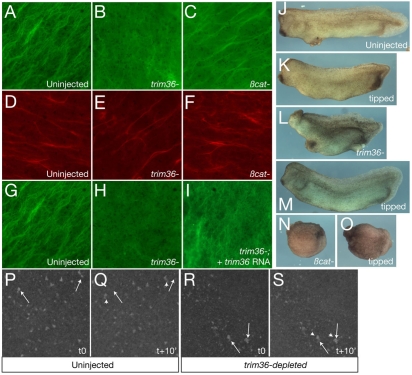
Fig. 6.
Trim36 regulates vegetal microtuble formation and cortical rotation. (A-C) Immunostaining of microtubules at 80 minutes post fertilization in control (A, uninjected), trim36-depleted (B, trim36-) and β-catenin-depleted (C, βcat-) eggs. (D-F) Immunostaining of cytokeratin at 80 minutes post fertilization in control (D, uninjected), trim36-depleted (E, trim36-) and β-catenin-depleted (F, βcat-) eggs. (G-I) Immunostaining of microtubules at 80 minutes post fertilization in control (G, uninjected), trim36-depleted (H, trim36-) and rescued (I, trim36-; + trim36 RNA) eggs. Vegetal views are shown in A-I, viewed with a 63× objective. (J-O) Representative phenotypes of uninjected (J,K), trim36-depleted (trim36-; L,M) and β-catenin-depleted (βcat-; N,O) embryos. (J,L,N) Normal orientation, (K,M,O) tilted 90°. (P-S) Frames from time-lapse movies of cortical rotation in DiOC6(3)-stained eggs. Controls (P,Q) and trim36-depleted (R,S) embryos at time 0 (t0) and +10 minutes (t+10′). Arrows indicate the starting points of indicated germ-plasm islands, arrowheads indicate the final position of the same islands. Images were taken with a 10× objective.