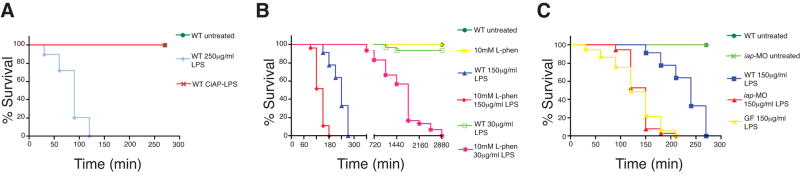
Figure 3.
Iap functions to detoxify LPS. (A) LPS pretreated with CIAP was non-toxic to zebrafish at 250 μg/ml LPS, in contrast to mock treated LPS. Inhibition of IAP activity using (B) L-phen, or (C) with iap-MO or by rearing larvae GF, significantly increased susceptibility of larvae to LPS killing. Survival curves are significantly different (except WT untreated and WT CIAP-LPS in A, WT untreated, 10mM L-phen and WT 30 μg/ml LPS in B, and iap-MO 150 μg/ml LPS and GF 150 μg/ml LPS in C, Logrank test, P < 0.0001). All animals were administered LPS at 7 dpf except in panel B, where animals exposed to 30 μg/ml LPS began treatment at 6 dpf. All animals were reared CV, unless otherwise indicated. n = at least 30 total animals for each sample group, in at least two independent trials.