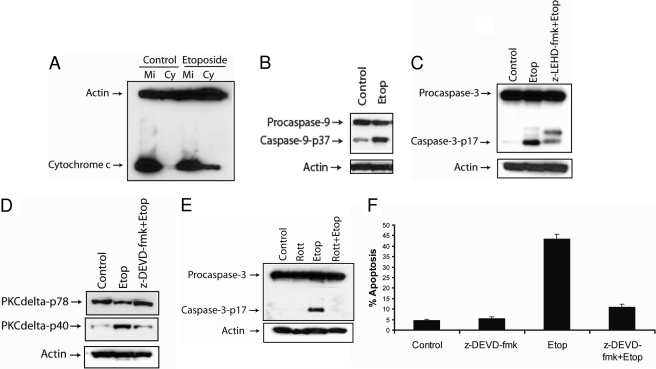
Fig. 3.
Etoposide triggers caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in SK-N-AS cells. A, cells were treated with 50 μM etoposide for 48 h and harvested. The cytosolic fractions were obtained by a digitonin-based subcellular fractionation procedure. One hundred micrograms of cytosolic (Cy) and mitochondrial protein fractions (Mi) was analyzed by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and cytochrome c and β-actin levels were determined by immunoblotting. B, immunoblot analysis of caspase-9 and β-actin in cell lysates treated with 50 μM etoposide for 48 h. C, immunoblot analysis of caspase-3 and β-actin in cell lysates treated with 50 μM etoposide with or without 20 μM caspase-9 inhibitor (z-LEHD-fmk) for 48 h. D, immunoblot analysis of PKCδ and β-actin in cell lysates treated with 50 μM etoposide with or without 20 μM caspase-3 inhibitor (z-DEVD-fmk) for 48 h. E, immunoblot analysis of caspase-3 and β-actin in cell lysates treated with or without 2 μM rottlerin, 50 μM etoposide, or 2 μM rottlerin and 50 μM etoposide for 48 h. F, cells were treated with 50 μM etoposide with or without 20 μM caspase-3 inhibitor (z-DEVD-fmk) for 48 h, and the percentage of apoptotic cells was quantified by counting fragmented nuclei stained with Hoechst 33342 among 200 cells. Shown are representative apoptosis rates from three independent counts.