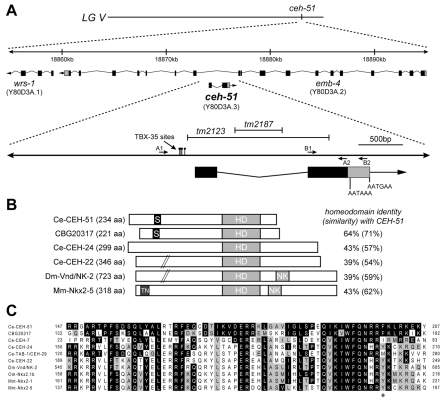
Fig. 2.
Structure of ceh-51 and its gene product. (A) Location of ceh-51 and emb-4 exons on LG V. The locations of the mutant alleles tm2123 and tm2187 and the primer pairs A1/A2 and B1/B2 (used to generate overlapping PCR products for rescue of tm2123) are shown. A 3′UTR of ∼260 bases is predicted by EST yk51g7. Polyadenylation motifs of AATAAA and AATGAA (Hajarnavis et al., 2004) are found 40 bp and 260 bp, respectively, downstream of the stop codon. tm2123 is a 1610 bp deletion that includes the coding portion of exon 1 and part of exon 2, including the first six amino acids of the predicted homeodomain, and carries an additional 14 bp insertion. The remainder of the ceh-51 coding region in tm2123 lacks any in-frame ATG codons, suggesting that tm2123 is null. tm2187 is an intronic 540 bp deletion and was not studied. (B) Comparison of CEH-51 and other NK-2 proteins. Like all C. elegans NK-2 factors, CEH-51 lacks the Tinman (TN) and NK-2-specific (NK) domains that are found in many other NK-2 factors (Harvey, 1996). Regions where at least 7/10 contiguous residues are serine are indicated by S. HD, homeodomain. (C) Homeodomain alignments. Identities with C. elegans CEH-51 are indicated by black boxes and similarities by gray boxes. A tyrosine residue found in NK-2 family members is indicated with an asterisk (Harvey, 1996). Accession numbers: C. elegans (Ce) CEH-51, CAB60440; CEH-7, AAC36745; CEH-24, AAB81844; TAB-1 (CEH-29), AAA98021; CEH-22, NP_001076744; C. briggsae CBG20317, CAP37360; Oncorhynchus mykiss (Om) Nkx2.1b, BAD93686; Mus musculus (Mm) Nkx2.1, NP_033411; Nkx2.5, NP_032726; Drosophila melanogaster (Dm) Vnd, P22808.