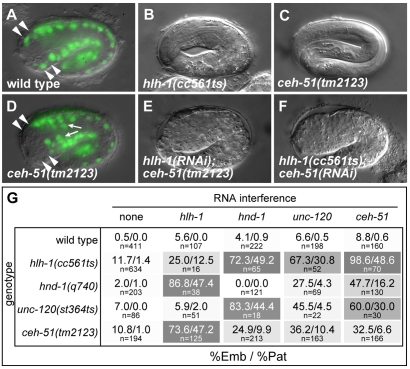
Fig. 7.
Muscle defects in ceh-51(tm2123). (A,D) Loss of MS-derived unc-120::GFP expression (arrowheads) in ceh-51 (D) as compared with wild type (A). Additional expression is indicated by small arrows. (B,C,E,F) Loss of ceh-51 synergizes with partial muscle specification mutants to produce paralyzed, arrested 2-fold (Pat) embryos. Whereas more than 95% of hlh-1(cc561ts) mutants grown at 15°C (B), and more than 99% of ceh-51(tm2123) embryos (C), elongated to greater than 3-fold, between 47 and 49% of embryos produced by a combination of mutation of ceh-51 with RNAi of hlh-1 (E), or vice versa (F), produced a synthetic Pat phenotype. (G) Summary of synthetic Pat phenotypes. Data are shown as the percentage of progeny arresting as embryos (%Emb)/percentage of progeny arresting as paralyzed, 2-fold (Pat) embryos (%Pat) (included in the Emb totals). Backgrounds have been shaded to indicate higher %Pat.