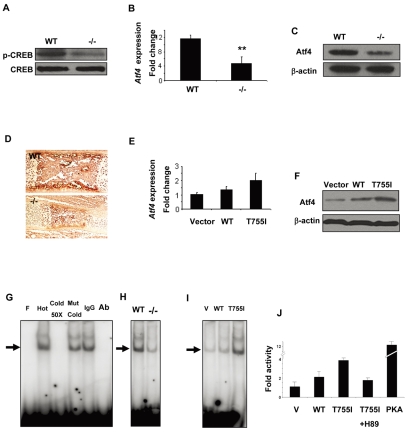
Fig. 7.
Regulation of Atf4 expression by Gpr48 through the cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling pathway. (A) Phosphorylated CREB (at Ser133) protein is decreased in Gpr48-/- calvarial osteoblasts; total CREB provides a loading control. (B,C) Deletion of Gpr48 decreases the expression level of Atf4 in calvarial osteoblasts at P4 as assessed by Q-PCR (B) and western blot (C). **P<0.01. (D) Decrease in Atf4 protein in Gpr48-/- mice at E16.5 as assessed by immunohistochemistry with specific anti-Atf4 antibody. (E,F) Overexpression of Gpr48 and its constitutively active form, T755I, increased the Atf4 expression level as measured by Q-PCR (E) and western blot (F). (G-I) Gpr48 regulates the binding of CREB to the CRE site in the Atf4 promoter as assessed by EMSA. (G) Direct binding of CREB transcription factor to the CRE site in the Atf4 promoter. F, free probe; Hot, hot probe; Cold 50×, cold competitors at a 50-fold excess; Mut Cold, mutant cold competitors; Ab, CREB antibody. (H) Deletion of Gpr48 decreased CREB binding to the Atf4 promoter in osteoprogenitor cell nuclear extracts as measured by EMSA. (I) Overexpression of Gpr48 and T755I increases CREB binding to the Atf4 promoter in Gpr48-transfected cell nuclear extracts. (J) Activation of the Atf4 promoter by Gpr48 and T755I through the PKA pathway. A constitutively active PKA subunit was used as a strong activator of the promoter. A specific inhibitor of PKA, H89, abolished the Gpr48-activated promoter activity. V, vector control.