Fig. 6.
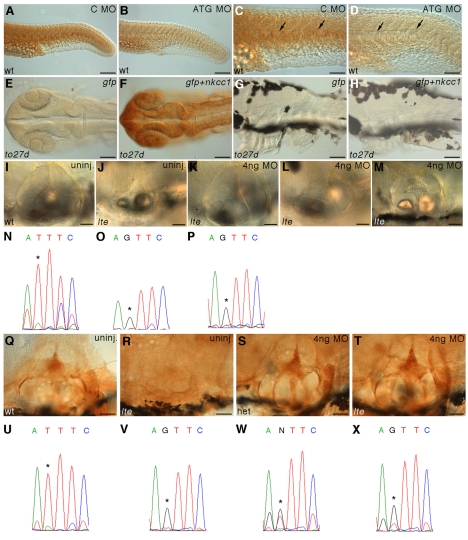
The lte phenotype can be rescued with a splice-blocking morpholino. (A-D) One nanogram of an ATG morpholino knocks down Nkcc1 protein expression in the notochord at 26 hpf (B; arrows in enlargement D) as compared with samples injected with 1 ng of a control morpholino (A; arrows in C). This reduction is not maintained at later stages and no phenocopy of the lte mutation was observed. (E-H) The lte phenotype cannot be rescued with a full-length mRNA encoding nkcc1. Ten picograms of Myc-tagged nkcc1 was injected alongside 10 pg gfp mRNA and embryos stained for Myc expression. At 26 hpf, cells are clearly positive for Myc, indicating expression of the tagged protein (F). Expression is extinguished by 74 hpf (H). No Myc expression is detected in embryos injected with gfp RNA alone (E,G). (I-X) A morpholino directed against the ectopic splice site in to27d can rescue the ear collapse phenotype at 6 dpf. Ear size in live injected mutants (K) can become indistinguishable from that of uninjected siblings (I) and is greatly increased compared with uninjected mutants (J). The sequencing traces (N-P,U-X) below each image confirm the genotype of the pictured embryos; the asterisk indicates the position of the mutation (T, wild-type allele; G, mutant allele). Examples of `mild' and `moderate' rescued embryos (see Table 1) are depicted in L and M, respectively; a rare complete rescue that would have been scored as `wild type' (Table 1) is shown in K. Rescue can also be seen at the protein level: T4 staining shows that an injected homozygous mutant (T) has similar levels of protein to an uninjected wild-type sibling (Q) or an injected heterozygous sibling (S). No antibody staining is present in the ear of an uninjected homozygous mutant (R). Scale bars: 100 μm in A-F; 50 μm in G-M,Q-T.