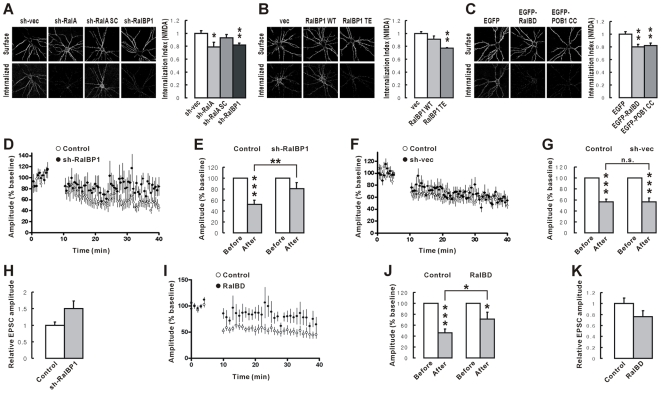
Figure 6. RalBP1 and RalA are required for NMDA-induced AMPAR endocytosis and LTD.
(A) Knockdown of RalBP1 and RalA suppresses NMDA-induced endocytosis of GluR2. Cultured neurons transfected with HA-GluR2+sh-(RalBP1, RalA, SC/scrambled, or vec/empty vector) (DIV 16–20) were subject to the antibody feeding assay under NMDA treatment condition (20 µM, 3 min). The internalization index (the ratio of internalized to internalized+surface receptors) was normalized to sh-vec control. n = 14–21, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, Student's t-test. (B) Overexpression of phosphomimetic RalBP1 TE (T645E), but not WT RalBP1, suppresses NMDA-induced GluR2 endocytosis. vec, vector alone. n = 17–22, ** p<0.01. (C) Overexpression of the RalBD and the POB1 CC, which inhibits RalA (active) and RalBP1, respectively, reduces NMDA-induced GluR2 endocytosis. n = 15–27, ** p<0.01. (D–G) RalBP1 knockdown suppresses paring-induced LTD at SC-CA1 synapses. CA1 pyramidal neurons in slice culture were transfected with sh-RalBP1 (D), or sh-vec (F) (DIV 3/4–6/7), followed by LTD induction by paring 300 pulses at 1 Hz at −45 mV. Average AMPAR EPSCs 25–30 min after LFS were measured from pairs of shRNA-expressing and untransfected neurons. Histograms (E and G) indicate EPSC amplitudes after LTD induction normalized to those before the induction (baseline). n = 10, *** p<0.001. The significance between the two LTD values was determined by Student's paired t-test. ** p<0.01, n.s., not significant. (H) Normal synaptic transmission in sh-RalBP1-expressing CA1 pyramidal neurons. EPSC amplitudes were normalized to untransfected control neurons in the same pair. (I–J) Overexpression of RalBD in CA1 pyramidal neurons reduces LTD at SC-CA1 synapses. n = 9, * p<0.05, *** p<0.001. The significance between the two LTD values was determined by Student's paired t-test. * p<0.05. (K) Normal synaptic transmission in RalBD-expressing neurons.