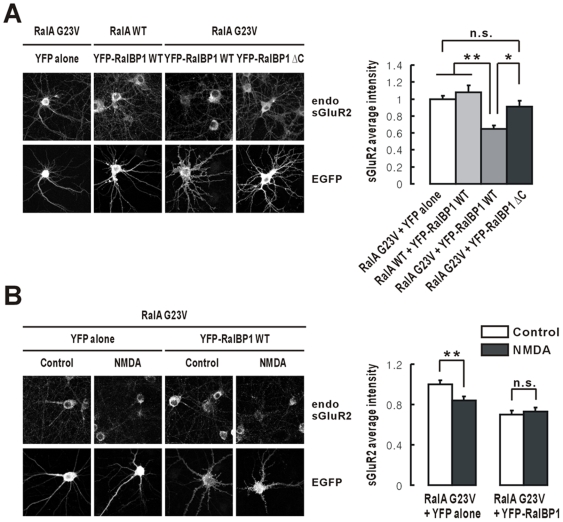
Figure 8. Constitutive RalA activation combined with RalBP1 binding to PSD-95 reduces surface AMPAR levels and occludes NMDA-induced AMPAR endocytosis.
(A) Constitutive RalA activation combined with RalBP1 binding to PSD-95 reduces surface levels of AMPARs (GluR2-containing endogenous receptors). Cultured neurons expressing RalA (G23V or WT)+YFP-RalBP1 (WT, ΔC, or YFP alone)+PSD-95 (C-terminally FRB tagged) (DIV 18–20) were stained for surface GluR2 (endogenous), EGFP (for YFP-RalBP1), and PSD-95 (unpublished data). PSD-95 was cotransfected to ensure that the amount of PSD-95 does not become a limiting factor for RalBP1 synaptically translocated by RalA G23V to interact with PSD-95. n = 10–16, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, ANOVA. n.s., not significant. (B) Constitutive RalA activation combined with RalBP1 binding to PSD-95 occludes NMDA-induced reduction in the levels of surface AMPARs. Neurons expressing RalA G23V+YFP-RalBP1 (or YFP alone)+PSD-95-FRB (DIV 18–20) were treated with NMDA (20 µM, 3 min), followed by 10 min incubation in the absence of NMDA and staining for surface GluR2 (endogenous), EGFP (for YFP-RalBP1), and PSD-95 (unpublished data). n = 10–13, ** p<0.01.